Imperialism: A System of “Antagonistic Cooperation” or of Antagonistic Contradictions?
Emperyalizm: Bir "Antagonistik İşbirliği" Sistemi mi Yoksa Antagonistik Çelişkiler Sistemi mi?
El imperialismo: ¿un sistema de “cooperación antagónica” o de contradicciones antagónicas?
Reply to a contribution of Promise Li to the Marxist imperialism theory
An Essay (with 8 Tables and 2 Figures) by Michael Pröbsting, 23 November 2024
Contents
Introduction
A brief summary of Li’s concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation“
Were Thalheimer and Bukharin really the pioneers of the concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation”?
A flawed methodological basis: Bukharin’s undialectical theory of equilibrium
A critique from the point of view of materialist dialectic
Capitalism in the 21st century: restoring its growth dynamic?
Do we overestimate the rise of Chinese and Russian imperialism?
Is capitalist interdependence an obstacle for inter-imperialist war?
Conclusions
* * * * *
Introduction
As I noted recently in a reply to the Argentinean economist Claudio Katz, the debate among Marxists about imperialism theory has intensified in the last few years. [1] A few weeks ago, another socialist writer, Promise Li, published a further contribution to this debate. [2]
Promise Li is a socialist from Hong Kong and now based in Los Angeles where he is active as a member of Tempest Collective and Solidarity (U.S.). His contribution is an elaboration of his concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation” which he delineates, on one hand, from those who consider the “US Empire” as the one and only imperialist force, and, on the other hand, from those who support Lenin’s orthodox imperialism theory. As he refers to me (correctly) as a supporter of the latter camp, I would like to respond to his criticism. I shall illustrate – both methodologically as well as empirically – that the concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation” does not allow to understand the dynamics of the world situation in the current period.
As this is a wide topic, I will try to limit myself to deal with the specific arguments and criticism presented by Li. For a more comprehensive elaboration of my understanding of the Marxist imperialism theory I refer readers to previous works. [3]
A brief summary of Li’s concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation“
First, I would like to note that Promise Li, in contrast to various other contributors to the debate, consistently rejects any accommodation to Chinese imperialism. As he noted in an interview, “the left must focus on building links between those resisting US and Chinese imperialisms.” [4] Hence, he positively delineates himself from (proto-)Stalinist writers who adhere to a one-eyed anti-imperialism which strongly denounces the crimes of Washington but is very restrained when it comes to the crimes of Beijing and Moscow. No doubt, Li’s first-hand experience with the brutal reality of the Xi regime in Hongkong has been pretty helpful for his understanding.
Nevertheless, his concept of imperialism is problematic as he downplays the accelerating inter-imperialist rivalry and overestimates the stability and cooperation between the Great Powers. In contrast, I consider the capitalist world system as one which is long-term decline. In such a period, the contradictions between imperialist powers in West and East (U.S., Western Europe, Japan, China and Russia) as well as between these powers and the semi-colonial countries can not but intensify. Imperialism is not a system characterised by “antagonistic cooperation” but rather by antagonistic contradictions.
Before discussing the flaws of the concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation”, we shall start with a summary of Li’s presentation. He relates the origins of his theory to the writings of German communist August Thalheimer and Nikolai Bukharin, a leading Bolshevik theorist. The concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation” was later revisited by Brazilian Marxist collective Política Operária (POLOP) to which belonged, among others, Ruy Mauro Marini, most known for his theory of sub-imperialism.
We note in passing that the theory of sub-imperialism, like the concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation”, lacks a dialectical approach. However, at this point we shall not discuss this issue and refer readers to other works in which we dealt with the theory of sub-imperialism. [5]
Starting from such methodological basis, Promise Li applies this concept to analyse the imperialist world order today. “[W]e can modify Thalheimer’s definition and consider antagonistic cooperation a particular stage of imperialism in which the terms for competition between national capitals take shape through or are mediated by the “interpenetration of mutual imperial interests and domains,” rather than cooperation and competition as distinct tendencies.”
Related to this, the author emphasizes the relative stability of the capitalist world system. Of course, he recognises its repeated crisis, however, he thinks that the tendency towards cooperation between the powers is prevailing.
“Without downplaying the ever-present threat of antagonistic crises and rivalries between states, this analysis foregrounds the capacity of the imperialist world system to maintain cooperative dynamics to maximize paths for global accumulation.”
Consequently, Li delineates his concept from other theories like, on one hand, that a “US-led Empire” would dominate the world and, on the other hand, from the orthodox Marxist imperialism theory.
“[W]e must not miss capitalism’s readjustment of its own constitution to develop new terms for recovery and stabilization. Antagonistic cooperation, a conceptual framework developed by Marxists in postwar Germany and Brazil, provides the best tools for analyzing this particular stage of imperialism. Unlike the unipolar theorization of Tricontinental or the multipolar rivalry of those following the Bolshevik theorists, which both overemphasize rivalry between imperialist powers, antagonistic cooperation understands the imperialist system as an interdependent totality that can accommodate interdependence between and beyond geopolitical blocs. Additionally, unlike the two models described above, antagonistic cooperation also allows for heterogeneity of power relations within this paradigm even as the overall structure of dependency between core and periphery economies continues to exist. For one, the rivalry between the United States and China does not imply their equality in the global imperialist system, which is still led and dominated by the former. What Claudio Katz calls “empires-in-formation,” and other intermediate or subimperial countries, are also cultivating the ability to occasionally check US power through military, economic, or other means. But this signals neither an anti-imperialist affront to US hegemony nor a straightforward leveling of the playing field as a new terrain of interimperialist rivalry.”
“Economic interdependence has shown surprising resilience even across rival geopolitical blocs. Existing theories of imperialism fail to fully account for these seemingly contradictory dimensions of today’s world system. Tricontinental theorizes the current stage of imperialism as “hyper-imperialism,” characterized by a unipolar “US-Led Military Bloc” as the sole imperialist force that renders all other global contradictions secondary or “non-antagonistic.” For the authors at Tricontinental, this imperialist bloc is being challenged by a multipolar “socialist grouping led by China,” representing “growing aspirations for national sovereignty, economic modernization, and multilateralism, emerging from the Global South.” Such a perspective disregards the implications of both the interdependence between the two blocs and the emergent role of certain intermediate economies — for example, Iran, the United Arab Emirates, and Russia — in developing regional hegemonies that facilitate imperialism amidst geopolitical tensions.
In contrast to Tricontinental, some see the form of imperialism today as an interimperialist conflict in the same vein as the First World War, which Bolshevik revolutionaries V. I. Lenin and Nikolai Bukharin first theorized. This view overly downplays the decline of US hegemony while overestimating the rise of new imperialists as a counterbalance to US imperialism. These faulty conceptions are two sides of the same coin: they overstate the dynamics of rivalry, thus obscuring salient sites of interconnection in the imperialist system that can yield powerful opportunities for solidarity across antisystemic struggles.”
Were Thalheimer and Bukharin really the pioneers of the concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation”?
Who were Bukharin and Thalheimer? Bukharin joined the Bolsheviks as a young and dedicated militant and worked in the Moscow underground party before joining other Russian revolutionaries in exile. He became a Bolshevik leader in 1917 and was a key figure in shaping the party’s policy in the first decade after the revolution. Bukharin was a gifted theoretician who repeatedly clashed with Lenin on issues like the imperialism theory, the state theory as well as the national question. Nevertheless, he was a thoughtful and inspiring Marxist intellectual and Lenin appreciated his work, calling him even “the darling of the party“.
While Bukharin was initially a spokesperson for the ultra-left wing in the party, he joined Stalin’s faction in 1923 and played a crucial role in theorizing the opportunist strategy of the Comintern, the pro-Kulak policy of the regime as well as the expulsion of the Left Opposition led by Leon Trotsky. However, soon after the repression of the authentic Bolsheviks in late 1927, the Stalinist bureaucracy, facing economic crisis as a result of their past pro-Kulak policy, turned towards forced collectivisation of the peasantry and super-industrialisation. Consequently, Stalin – whom Bukharin now realised to be a “new Genghis Khan” – also kicked out the former “darling of the party“. However, in contrast to the Trotskyists, Bukharin and his supporters refrained from launching an opposition struggle and quickly capitulated to Stalin. This was the end of Bukharin as an independent politician and a few years later, during the horrific show trials in 1936-38, they were all shot. [6]
August Thalheimer was part of the left-wing of German social democracy before 1914 who joined the Spartacus League of Rosa Luxemburg and Karl Liebknecht during World War I. He became the Communist Party’s leading theoretician in 1921 when he and Heinrich Brandler took over the leadership. However, as they miserably failed in the revolutionary situation in the second half of 1923 (the “German October” which did not take place), they had to retreat from leadership functions. After the downfall of their intellectual mentor Bukharin in 1928, Brandler and Thalheimer formed the so-called international Right Opposition which criticized the Stalinists only for its ultra-left (but not its opportunist) mistakes and failed to call for an opposition struggle against the regime. Worse, they fully supported the arch-opportunist people’s front policy in the mid-1930s and refused to condemn the Moscow show trials. Unsurprisingly, the international Right Opposition crumbled in the late 1930s and only a small group continued to exist in Germany after WWII. [7]
Despite their methodological failings, Bukharin and Thalheimer – the first much more than the latter – were serious theoreticians who made a number of thoughtful contributions.
Promise Li resp. the POLOP collective base their concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation” on a German-language pamphlet of Thalheimer – “Grundlinien und Grundbegriffe der Weltpolitik nach dem 2. WeItkrieg” (Basic Principles and Concepts of World Politics after World War II) – which he had published in 1946. In this pamphlet, the German communist called the imperialist alliance led by the U.S. as “antagonistic cooperation”.
However, while it is true that this term originates from Thalheimer’s pamphlet, POLOP’s resp. Li’s reference to this document is highly problematic. In this work, the German communist viewed his term “antagonistic cooperation” as a description of the situation after WWII. But he recognised that the cooperation between the imperialist powers was based a) on the overriding class contradictions between the Western powers and the expanding Stalinist camp and b) on the absolute superiority of the U.S. Hence his analysis of inter-imperialist cooperation was based on these conjunctural features.
Consequently, Thalheimer’s view of the world order was not one of “cooperation” but rather of looming World War III as the imperialist alliance was based on collective aggression against the Stalinist camp, i.e. the degenerated workers states.
“We have shown factors that have caused that the imperialists’ urge for territorial expansion does not result in war within the capitalist camp but rather primarily in imperialist cooperation in different degrees. Therefore, this urge for territorial expansion can only be directed externally: against the socialist sector, the Soviet Union and its sphere of influence.”
“If these facts show anything it is, in the immediate aftermath of World War II, the ongoing general deployment for a new world war.” [8]
However, Promise Li’s understanding of concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation” is a different one. Such cooperation can no longer be based on a common policy of aggression against a joint enemy since the USSR and its allies do no longer exist for three decades. Hence, Li views “antagonistic cooperation” as a new stage of imperialism – independent on the existence of a common enemy which would keep the imperialist powers united (like the Stalinist camp led by the USSR in 1945-91). In contrast, Thalheimer elaborated his concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation” as a conjunctural description of a specific situation caused by the peculiar features of the outcome of World War II. For the German communist, such a situation of “antagonistic cooperation” would not longer exist when the common enemy had disappeared.
Likewise, Bukharin peculiar analysis of imperialism, certainly not without flaws, had definitely no approach which came close to a concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation” as advocated by Li. Far from assuming a relatively stable world or even a prevailing cooperation between the Great Powers, he rather viewed imperialism as an antagonistic system characterised by sharp inter-imperialist rivalry and a tendency towards war between these.
“From the point of view of the ruling circles of society, frictions and conflicts between "national" groups of the bourgeoisie, inevitably arising inside of present-day society, lead in their further development to war as the only solution of the problem. We have seen that those frictions and conflicts are caused by the changes that have taken place in the conditions of reproducing world capital. Capitalist society, built on a number of antagonistic elements, can maintain a relative equilibrium only at the price of painful crises.“ [9]
“The transition to a system of finance capitalism constantly reinforced the process whereby simple market, horizontal, competition was transformed into complex competition. Since the method of struggle corresponds to the type of competition, this was inevitably followed by the ‘aggravation’ of relations on the world market. Methods of direct pressure accompany vertical and horizontal competition, therefore the system of world finance capital inevitably involves an armed struggle between imperialist rivals. And here lies the fundamental roots of imperialism. (…) The conflict between the development of the productive forces and the capitalist relations of production must - so long as the whole system does not blow up - temporarily reduce the productive forces so that the next cycle of their development might then begin in the very same capitalist carapace. This destruction of the productive forces constitutes the conditio sine qua non of capitalist development and from this point of view crises, the costs of competition and - a particular instance of those costs - wars are the inevitable faux frais of capitalist reproduction.” [10]
As we can see, Bukharin – in contrast to Li – did not view the internationalisation of capitalist production and reproduction as a feature which would limit the inter-imperialist tensions. He rather understood it as a development which would accelerate the conflicts between the Great Powers.
“The international division of labour, the difference in natural and social conditions, are an economic prius which cannot be destroyed, even by the World War. This being so, there exist definite value relations and, as their consequence, conditions for the realization of a maximum of profit in international transactions. Not economic self-sufficiency, but an intensification of international relations, accompanied by a simultaneous "national" consolidation and ripening of new conflicts on the basis of world competition—such is the road of future evolution.“ [11]
Hence, the Bolshevik theoretician characterised war as an “immanent law” of imperialism: “War in capitalist society is only one of the methods of capitalist competition, when the latter extends to the sphere of world economy. This is why war is an immanent law of a society producing goods under the pressure of the blind laws of a spontaneously developing world market, but it cannot be the law of a society that consciously regulates the process of production and distribution.“ [12]
In summary, we think the Li’s resp. POLOP’s reference to Thalheimer and Bukharin as pioneers of the concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation” lacks justification.
A flawed methodological basis: Bukharin’s undialectical theory of equilibrium
Having said this, we do not deny that there also exists an element of justification when Li points to the writings of Bukharin and Thalheimer. This is because the concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation” shares certain methodological similarities in their mode of thinking with these two theoreticians. Namely, they all embrace – consciously or unconsciously – the mechanist equilibrium theory which is devoid of dialectics.
As quoted above, Li’s “analysis foregrounds the capacity of the imperialist world system to maintain cooperative dynamics to maximize paths for global accumulation.” Likewise, he quotes approvingly another writer saying that “cooperation [between the imperialists, Ed.] for the maintenance of the system prevails“:
“As Sachs writes: ‘Antagonistic cooperation does not free the capitalist world from internal shocks at all levels, ups and downs. There are moments when antagonism seems to predominate, when the national bourgeoisies threaten an “independent” foreign policy, rebel against the schemes of the International Monetary Fund, and nationalize particularly unpopular foreign companies. The same phenomenon occurs among the imperialist powers themselves in moments of periodic relaxation of international tension. It disappears when there is a new upsurge in international tension and, as in France in 1968, when the capitalist regime is put in check. In the long run, cooperation for the maintenance of the system prevails.’”
While, as mentioned before, Bukharin disagreed with any view of the imperialist world as one of cooperation, he indeed sympathized with the philosophical teachings of Alexander Bogdanov who opposed dialectical materialism and elaborated a system called “organizational philosophy”. Bogdanov was a leading figure among the Bolsheviks in the years 1904-08 but Lenin had to wage a fierce struggle against him and his philosophy when the political differences – he combined his idealist philosophy with support for ultra-left politics after the defeat of the first Russian Revolution in 1905-07 – threatened to paralyze the party. Lenin’s famous philosophical work “Materialism and Empirio-criticism” is basically a polemic against Bogdanov’s philosophy which lacked both materialism as well as dialectics. [13]
Bukharin – about whom Lenin noted in his testament that “he has never made a study of dialectics, and, I think, never fully appreciated it” – adopted Bogdanov’s equilibrium theory. This theory basically considers reality as a (relative, moving) equilibrium which, repeatedly, gets disrupted by sudden crisis and, after some time, restabilises as a new equilibrium. In other words, equilibrium would be the natural position of things. In his book “Historical Materialism” Bukharin expresses such a view quiet explicitly.
“On the other hand, we have here also the form of this process: in the first place, the condition of equilibrium; in the second place, a disturbance of this equilibrium; in the third place, the reestablishment of equilibrium on a new basis. And then the story begins all over again: the new equilibrium is the point of departure for a new disturbance, which in turn is followed by another state of equilibrium, etc., ad infinitum.” [14]
This does not mean that Bukharin ignored contradictions and the resulting motion as crucial driving forces of development. However, he viewed contradictions not so much as an internal, essential feature of all things (including an equilibrium) but rather as something external. This is because he ignored the unity of opposites and the struggle between its contradictory parts as the fundamental law to understand matter and its motion. “Development is the “struggle” of opposites“ – as Lenin said. [15] Hence, for Bukharin motion was not so much caused by internal contradictions but rather by contradictions between different things (equilibriums).
Such he wrote in said book. “If, in a condition of growth, the structure of society should become poorer, i.e., its internal disorders grow worse, this would be equivalent to the appearance of a new contradiction: a contradiction between the external and the internal equilibrium, which would require the society, if it is to continue growing, to undertake a reconstruction, i.e., its internal structure must adapt itself to the character of the external equilibrium. Consequently, the internal (structural) equilibrium is a quantity which depends on the external equilibrium (is a "function" of this external equilibrium).” [16]
“The precise conception of equilibrium is about as follows: "We say of a system that it is in a state of equilibrium when the system cannot of itself, i.e., without supplying energy to it from without, emerge from this state.“ [17]
Of course, Bukharin did not explicitly deny the role of internal contradictions. He was too much a smart Marxist intellectual for this. But despite his intentions, he systematically underestimated the decisive role of internal contradictions as the primary driving force of motion.
A critique from the point of view of materialist dialectic
The connection between the mechanist equilibrium theory of Bukharin and the concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation” becomes already clear. The philosophy of downplaying the struggle of opposites and of internal contradictions causing motion results in an understanding of reality as a state of (moving) equilibrium. On such a methodological basis, one ends up easily in viewing the world situation as one primarily characterised by relative stability and cooperation between the imperialists. As a result, one gets confused and can not recognise the direction of motion of world politics and economy.
The mechanist method is incapable of answering correctly a crucial question: what is the determining characteristic of matter – a state of equilibrium or contradiction, motion as a result of the struggle of opposites? From the point of view of materialist dialectic, the correct answer is that the struggle of opposites, contradiction is the determining feature since it causes motion, transformation, progress. In contrast, the state of equilibrium is only a temporary moment. Hegel was absolutely right when he noted: ”Contradiction is the root of all movement and vitality, and it is only insofar as it contains a Contradiction that anything moves and has impulse and activity.“ [18]
This was also the understanding of Marx and Engels. The latter explained in his “Anti-Dühring”:
„Motion is the mode of existence of matter. Never anywhere has there been matter without motion, nor can there be. Motion in cosmic space, mechanical motion of smaller masses on the various celestial bodies, the vibration of molecules as heat or as electrical or magnetic currents, chemical disintegration and combination, organic life -at each given moment each individual atom of matter in the world is in one or other of these forms of motion , or in several forms at once. All rest, all equilibrium, is only relative, only has meaning in relation to one or other definite form of motion. (...) Matter without motion is just as inconceivable as motion without matter. Motion is therefore as uncreatable and indestructible as matter itself.“ [19]
Based on such an approach, Lenin emphasised in his article “On the Question of Dialectics” that motion and the struggle between the opposites are absolute while stability, unity of opposites is relative.
„The unity (coincidence, identity, equal action) of opposites is conditional, temporary, transitory, relative. The struggle of mutually exclusive opposites is absolute, just as development and motion are absolute.“ [20]
Hence, materialist dialectic refuses to view equilibrium as the “normal” or “basic” condition of matter. It is rather a temporary stage in a long process of motion. As Engels noted in his preliminary studies for his “Dialectics of Nature”:
“[T]he individual motion strives towards equilibrium, the motion as a whole once more destroys the individual equilibrium. (…) All equilibrium is only relative and temporary.“ [21]
It is now possible to better understand the category of equilibrium. Marxists don’t deny the legitimacy of such category. But it must be understood properly. Motion does not take place in vacuum. It is caused by the struggle of opposites. Such struggle can only take place if there is a relationship between these opposites. The totality of such relationships constitutes a kind of (temporary) equilibrium. But such relationship is in constant motion because “reality is a ‚process of creation and destruction’“ – as Abram Deborin, the leading philosopher of the great dialectical school which dominated the philosophical discussions in the young Soviet Union in the 1920s before it was crushed by Stalin, noted. [22]
Therefore, from the point of view of materialist dialectic, there exists a clear dialectical hierarchy. N.A. Karev, another leading philosopher of the Deborin school and a supporter of Trotsky’s Left Opposition, explained in a critique of Bogdanov’s equilibrium theory:
“Hence, Engels does not say at all that this or that state of equilibrium would not exist in reality. But they are provisional, they only constitute moments in the motion of matters, they make sense only in relations to this or that form of moments, they are the result of a limited motion. Hence, the states of equilibrium are subordinated and temporary moments in the process of motion and development. The fundamental and determining is the motion.“ [23]
Karev’s critique of Bogdanov seems to us also very appropriate to the concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation” as it is advocated by Promise Li and POLOP.
„Bogdanov’s theory of equilibrium basically rests on the static point of view and not the dynamic one, as it recognizes the moment of static state as determining and not the moment of motion of a given body. The category of ‘moving’ equilibrium does not solve the problem as it view the mobility as a breach of the equilibrium and not the other way round – that the state of equilibrium is a provisional and relative moment of stability within the process of motion. The unity of equilibrium and motion is here understood by emphasizing the category of equilibrium while dialectic emphasizes the motion of a body, which is always and everywhere inherent to it.“ [24]
This brings us to the last point of our brief philosophical excursus. Underestimating the centrality of struggle of opposites resulting in motion and overemphasizing the concept of equilibrium results in inability to assess the dynamic and direction of development. For a mechanist, who is fixated to the state of equilibrium, things appear as static, not much in motion. In reality, profound developments take place “below the surface” which can only be recognized by dialectically approaching a given state of things (an “equilibrium”) as a temporary expression of motions caused by the struggle of opposites.
To give a simple analogy from daily life. If one is cooking water at home, one won’t observe big changes most of the time. The water appears unvaried … until the final moments when it starts boiling. Does this mean that for 99% of the time, nothing is happening, and the water is just in a state of equilibrium? Well, you don’t need a doctor’s degree in physics to know that this is not the case but that a “hidden” process of heating is taking place in this period.
Similarly, Marxists analysing the developments in world politics and economy must not stop in observing only those phenomena which appear at the surface. They must look below the surface and identify the processes of accumulating contradictions in order to understand the direction of development with ruptures and explosions ahead. As Deborin once said: „First and foremost, a Marxist must determine the general direction of development.“ [25]
However, this is only possible if one applies a materialist and dialectical method and avoids the doctrinaire schemas of mechanist equilibrium theory which are just painting an illusionary picture of drowsy stagnation. Hegel noted that the method is the “soul and substance” and that “anything whatever is comprehended and known in its truth only when it is completely subjugated to the method“ [26] And indeed, without the method of materialist dialectic, one is lost to understand the dynamic of modern imperialism.
In the end, the mechanist method a la Bukharin obstructs the recognition of the decay of capitalism and the accompanying processes of wars, revolutions and counterrevolutions.
Capitalism in the 21st century: restoring its growth dynamic?
As already mentioned above, Promise Li emphasizes in his essay that the elements of cooperation between imperialist powers (and also with national bourgeoisies in the Global South) are prevailing. Likewise, while he recognizes that capitalism is facing repeated crises, he believes that it has also shown the capacity to overcome these and to restore growth (albeit he says that this is not an automatic process but needs political intervention).
“However, we must also not mistake this interdependence for an inert tendency of the system toward equilibrium. In reality, the maintenance of this cooperation requires continual upkeep, especially as the capitalist system is forced to address the repeating appearance of crises stemming from its internal contradictions. The crises of profitability in the 1970s and the 2000s, for example, required fundamental transformations in how capitalism is organized in order to restore growth (and the suppression of working-class insurgency). Thus, the terms for cooperation must be consciously reinvented to be maintained.”
In contrast, we think that capitalism has entered a long-term period of crisis – or a “curve of decline” (to use a category from Trotsky’s concept of “curves of capitalist development” which he elaborated in a thoughtful article in 1923) – in the mid-1970s. [27] This process of crisis has deepened since the Great Recession in 2008/09 and the new period since then. [28]
Naturally such decay is not a linear process since a) capitalist reproduction proceeds in business cycles with ups and downs and b) there exist also counter-veiling tendencies. However, in the long run, the tendency of decline prevails, and this is a process which can be detected by numerous facts.
Most importantly, there exists a profound civilization crisis reflected in the devastating climate change with catastrophic consequences for growing parts of humanity. [29] Likewise, there is a clear tendency towards stagnation and decline in the capitalist world economy, resulting in growing waves of migration, social misery and more wars. Related to the same process is the accelerating militarization and rivalry between the imperialist powers. Two major wars – in the Middle East and Ukraine – with both having Great Powers, directly or indirectly, involved and with the potential to spread to other countries are powerful examples for this.
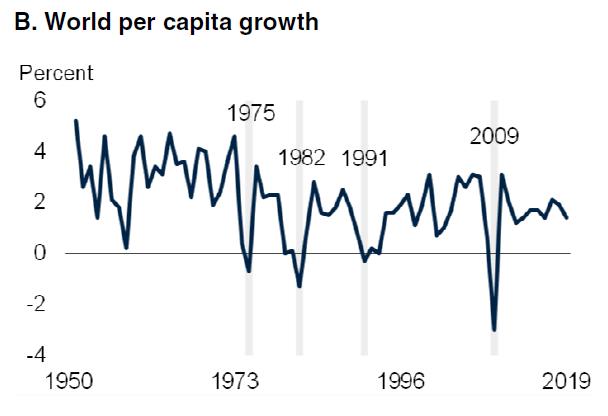
Since we have dealt with these issues on various occasions, we shall limit ourselves to presenting a few figures which demonstrate the declining dynamic of the capitalist world economy. As we can see from the figures in Table 1 and Figure 1, there has been a continuous decline of the growth rates of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) – both in total as well as per capita – since the 1950s. One should note that these tables do not include the figures for the Great Depression of the world economy which started in late 2019 and which included the worst slump since 1929.
Table 1: Average Annual Growth of Global GDP 1960-2019 [30]
1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s 2011-17 2019
4.9% 3.93% 2.95% 2.70% 2.58% 2.75% 2.5%
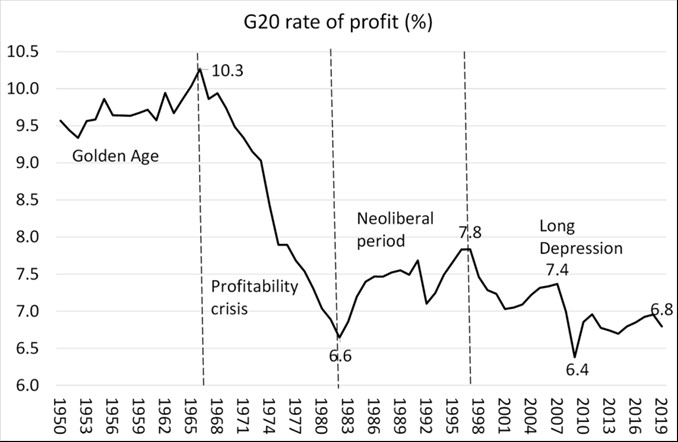
Such decline of the growth rates of capitalist economies goes hand in hand with, or has rather been caused by, a corresponding decline of the profit rate – which is, ultimately, the result of the declining share of living labour and the rising share of dead labour (machines and raw materials) in total capital. As Marx once noted, ”this law, and it is the most important law of political economy, is that the rate of profit has a tendency to fall with the progress of capitalist production.“ [32]
In Figure 2 we show the development of the profit rate in the 20 largest economies (G20 states) in the last seven decades. As we can see, there has been, as Marx predicted, such a long-term tendency of the profit rate in the last seven decades.
Hence, we can see clearly that world capitalism has not restored its growth rates of earlier times – despite numerous political interventions by the ruling class and despite “antagonistic cooperation”. It remains trapped in a long-time period of stagnation and decline.
Do we overestimate the rise of Chinese and Russian imperialism?
As the quote above shows, Li believes that I and likeminded writers would “overly downplays the decline of US hegemony while overestimating the rise of new imperialists as a counterbalance to US imperialism”. Unfortunately, he does not provide a single quote to proof his claim. Hence, I have not the slightest idea why Li thinks that I underestimate the decline of US hegemony. In any case, I think his criticism is not justified.
We did show in a number of works, China’s capitalist class could not only massively enrich itself at the cost of the domestic working class but has also been able to challenge the U.S. on the world market. Again, I limit myself to demonstrate this development with a few figures and refer interested readers to more elaborate studies. [34]
In the tables below we show that China has rapidly caught up with the long-time hegemon – U.S. imperialism. In Table 2 we see that China’s share in global manufacturing output was less than half of the U.S. in the year 2000 (9.8% vs. 23.7%); however, by 2022, its share was already nearly double as big as that of its Western rival (30.7% vs. 16.1%).
Table 2. Top Six Countries in Global Manufacturing, 2000 and 2022 [35]
Rank Country Share 2000 Share 2022
1. China 9.8% 30.7%
2. U.S. 23.7% 16.1%
3. Japan 10.2% 6.0%
4. Germany 6.4% 4.8%
5. South Korea 2.5% 3.1%
6. India 1.4% 3.1%
We see a similar picture when we look at the national composition of the world’s leading corporations as well as the global ranking of billionaires (Table 3-5). In all these categories, China has become No.1 or 2 – ahead or behind the U.S.
Table 3. Top 10 Countries with the Ranking of Fortune Global 500 Companies (2023) [36]
Rank Country Companies Share (in%)
1 United States 136 27.2%
2 China (excl. Taiwan) 135 27.0%
3 Japan 41 8.2%
4 Germany 30 6.0%
5 France 23 4.6%
6 South Korea 18 3.6%
7 United Kingdom 15 3.0%
8 Canada 14 2.8%
9 Switzerland 11 2.2%
10 Netherlands 10 2.0%
Table 4. Top 5 Countries of the Forbes Billionaires 2023 List [37]
Rank Country Number of billionaires
1 United States 735
2 China (incl. Hong Kong) 561
3 India 169
4 Germany 126
5 Russia 105
Table 5. Top 10 Countries of the Hurun Global Rich List 2024 [38]
Rank Country Number of billionaires
1 China (incl. Hong Kong) 814
2 U.S. 800
3 India 271
4 United Kingdom 146
5 Germany 140
6. Switzerland 106
7. Russia 76
8. Italy 69
9. France 68
10. Brazil 64
Russia has also developed a monopoly capital which dominates the domestic market and which exports capital to various other countries – mainly in Central Asia and Eastern Europe. Its economic strength has also been demonstrated by the fact that it has managed to resist an unprecedented wave of sanctions by all Western powers – because of the Ukraine War – since nearly three years. However, its position on the world market is substantially weaker albeit it has recently surpassed Germany’s and Japan’s GDP in PPP terms (Purchase Power Parity). [39]
While Russia is economically clearly behind the U.S. and China, it is a leading force in the military field. It has the largest nuclear arsenal and the third highest military expenditure. (See Table 6 and 7) Furthermore, it has demonstrated its military aggressiveness in numerous military interventions in other countries in order to expand its influence, to put down popular rebellions or to keep an allied dictatorship in power (e.g. Chechnya, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Syria, Libya, Mali, etc.) [40]
Table 6. World Nuclear Forces, 2024 [41]
Country Total Military Stockpile Total Inventory (incl. Retired Warheads)
Russia 4,380 5,580
United States 3,708 5,044
China 500 500
France 280 290
United Kingdom 225 225
India 172 172
Pakistan 170 170
Israel 90 90
North Korea 50 50
Table 7. Military Expenditure, in Billion US-Dollar as Share of World Spending, 2023 [42]
Spending ($ billion) Share of World Spending
1. United States 916 37%
2. China 296 12%
3. Russia 109 4.5%
Furthermore, China and Russia have recently substantially expanded their spheres of influence as the enlargement of BRICS shows. Four states – Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran and United Arab Emirates – formally joined the five original BRICS members (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) at the beginning of 2024. One country, Saudi Arabia, has been invited to join but has still not decided on this. And in October 2024, 13 other states became so-called “partner countries” (Algeria, Belarus, Bolivia, Cuba, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Nigeria, Thailand, Türkiye, Uganda, Uzbekistan, and Vietnam).
As I did elaborate in more detail in my above-mentioned reply to Claudi Katz, BRICS+ had, after its expansion to nine member states in 2023, a combined population of about 3.5 billion, or 45% of the world’s people (and it is now more than half if one includes the new “partner countries”). Its combined GDP – depending on the method of calculation – is either a bit more than 1/3 behind the Western Great Powers (G7) or has already surpassed the old imperialist powers. Likewise, BRICS+ accounts for 38.3% of the total world industrial production – the main sector of capitalist value production.
As for energy sources, the BRICS+ members own 47% of the world's oil reserves and 50% of its natural gas reserves. [43] As of 2024, the BRICS, along with their new members, control approximately 72% of the world's rare earth metal reserves. [44]
Of course, it is true that BRICS+ is not a homogenous and centralized alliance. Still, it is a “a non-western group", as Modi and Putin emphasised, which is dominated by Chinese and Russian imperialism. Furthermore, the BRICS+ countries are capitalistically less developed and have a lower living standard.
Nevertheless, while Li thinks that I overestimate the rise of China and Russia as new imperialist powers, I rather think that he underestimates this process and, as a result, also underestimates the acceleration of the inter-imperialist rivalry. The military threats and nuclear sabre rattle between NATO and Russia as well as the accelerating military tensions between Washington and Beijing in the South China Sea resp. around Taiwan are clear indications that the imperialist system is not so much characterised by “antagonistic cooperation” but rather by antagonistic contradictions.
It is therefore hardly surprising that, as SIPRI reports, global military expenditure rises year for year since the mid-1990s and is now – with a total of $2,443 billion – about double as high as it was 30 years ago. [45]
The accelerating inter-imperialist rivalry is not limited to armament and military tensions. There is also an escalating trade war between the U.S., China, EU and Russia combined with rising protectionism. In fact, globalisation has ended since the Great Recession in 2008 after decades of massive growth (“Globalization”). Since then, i.e. for more than 15 years, world merchandise trade has declined as a share of global output from 51.2% (2008) to 45.8% (2023). [46]
So, when Li says that “far from undoing the neoliberal world order, the capitalist class innovates new terms for maintaining and reforming globalization”, he completely misunderstands the direction of development of relations between imperialist powers.
For all these reasons, it is difficult to understand why Li objects to the category of a “new Cold War” between the Western and Eastern powers, calling it an “ideological fiction”. Does he not see the rising militarism and acceleration of rivalry which are all pointing to another world war between the imperialist powers?
As I insisted before, Marxists must “determine the general direction of development” in order to understand the coming ruptures and explosions. Li’s concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation” does not help in understanding the dynamics of the current world situation.
Is capitalist interdependence an obstacle for inter-imperialist war?
Let us finally deal with another important argument which Li raises in his essay. As shown in the quotes above, he argues that “economic interdependence” has been a key feature of modern imperialism and, as a result, this would constitute the material basis for “antagonistic cooperation” between the powers. He even thinks that such economic interdependence would make an inter-imperialist war impossible or at least unlikely.
“Indeed, global economic integration still existed in salient forms during the First World War, but mostly just contained within geopolitical camps, which historian Jamie Martin calls “strained interdependence.” However, the rise of neoliberalism has developed a level of interdependence that endures even across rival state blocs, thus undercutting the possibility of open interimperialist warfare witnessed in the first two World Wars.”
We think that this is wrong – both methodologically as well as historically. As Bukharin correctly pointed out in the above-mentioned quotes, interdependence not only deepens economic links but also accelerates rivalry. In the past years, China and the U.S. have been among the most important trading partners of each other. This has, however, not prevented these powers from starting and accelerating a trade war. The same is now the case between China and the European Union where the latter has imposed substantial tariffs on Chinese imports. True, big business on both sides is not happy about this development. But in the end, they have to subordinate to the objective laws of capitalism and its inherent inter-imperialist rivalry.
As I discussed in my above-mentioned book about Great Power rivalry, there exists also a historic precedent for such a development. Britain and Germany, two major rivals in World War I, had close economic relations before 1914. [47] In Table 8 we see that Britain was Germany’s most important trade partner before 1914 (and the U.S. was No. 2) while Germany was nearly as important as France for Britain’s trade. However, such economic interdependence did not prevent these powers from launching the most devastating war against each other.
Table 8. Main Trade Partners of Britain and Germany, 1890-1913 (Average % Share) [48]
Britain Germany
1. U.S.: 19.47% 1. Britain: 13.85%
2. France: 8.99% 2. U.S.: 11.03%
3. Germany: 8.90% 3. Austria-Hungary: 10.15 %
Hence, in the long run, increasing economic interdependence between imperialist powers does not result in a more stable capitalist world system. It does not create a type of imperialism characterised by “antagonistic cooperation”; imperialism remains rather a system full of antagonistic contradictions.
Conclusions
1. The concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation“ does not allow to understand the dynamics of the world situation in the current period. While Promise Li correctly recognises the imperialist nature not only of the old Western but also of the new Eastern powers (China and Russia), he mistakenly criticises supporters of the orthodox theory of imperialism of overestimating the rivalry between these.
2. The reference of Promise Li and the Brazilian collective Política Operária to August Thalheimer and Nikolai Bukharin as pioneers of the concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation“ is misleading. Bukharin, despite his weaknesses of schematism, emphasised the rivalry and antagonism between the imperialist powers which inevitable had to result in wars. It is true that Thalheimer elaborated the thesis of “antagonistic cooperation“ between imperialist powers in 1946. But this was a (correct) description of a specific global situation characterised by a) the massive expansion of the Stalinist states and b) the outcome of World War II with the U.S. as the absolute hegemon among the imperialist states. Hence, his thesis of more cooperation between the imperialist powers was directly related to their collective aggressive approach against the Stalinist states which was pointing to a new world war. Therefore, Thalheimer’s considered that the inter-imperialist tensions would be reduced because they were overridden by the massive acceleration of tensions between the imperialist and the degenerated workers states. However, since Stalinism collapsed in 1989-91, Thalheimer’s concept is no longer applicable for imperialism today.
3. It is true that Bukharin, the political mentor of Thalheimer, was influenced by the philosophy of Alexander Bogdanov, a staunch opponent of dialectical materialism. Hence, he advocated a world view which incorporated the mechanist equilibrium theory – a concept which downplays the role of internal contradictions as the driving force of motion. Consequently, supporters of such method consider equilibrium as the main feature of matter while, in fact, it is rather motion. Hence, the Bukharinite method underestimates the tendencies of rupture, crisis and explosions in the world situation and overestimates its stability and equilibrium. The concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation“ suffers from such methodological deficits.
4. From the point of view of materialist dialectic, internal contradictions, caused by the unity and struggle of opposites, are the driving force of motion. The mechanist method is incapable of answering the question correctly: what is the determining characteristic of matter – a state of equilibrium or contradiction, motion as a result of the struggle of opposites? From the point of view of materialist dialectic, the correct answer is that the struggle of opposites, contradiction is the determining feature since it causes motion, transformation, progress. In contrast, the state of equilibrium is only a temporary moment.
5. There is a clear connection between the mechanist equilibrium theory of Bukharin and the concept of imperialism as “antagonistic cooperation”. The philosophy of downplaying the struggle of opposites and of internal contradictions causing motion results in an understanding of reality as a state of (moving) equilibrium. On such a methodological basis, one ends up easily in viewing the world situation as one primarily characterised by relative stability and cooperation between the imperialists. As a result, one gets confused and can not recognise the direction of motion of world politics and economy.
6. Consequently, Promise Li does not sufficiently take into account the crisis-ridden character and the decay of the imperialist world system – both economically as well as politically. The capitalist world economy is trapped in long-term stagnation and decline, climate change is threatening the survival of humanity, and social misery and wars are spreading.
7. The criticism of Promise Li that we would overestimate the rise of Chinese and Russian imperialism ignores the qualitative changes in the relation of forces between the Great Powers in the past one, two decades. The Eastern imperialists are seriously challenging the long-time Western hegemony – economically, political and militarily. In fact, Li’s critique is related to his underestimation of inter-imperialist rivalry and his view that “antagonistic cooperation“ would be the main feature of the world situation.
8. Promise Li claims that “economic interdependence” is a key feature of modern capitalism and that this would “undercut the possibility of open inter-imperialist warfare”. However, history has shown that this is not true. In the long run, increasing economic interdependence between imperialist powers does not result in a more stable capitalist world system. It does not create a type of imperialism characterised by “antagonistic cooperation”; imperialism remains rather a system full of antagonistic contradictions.
[1] Michael Pröbsting: Are we living in the Age of “Empire” or of Imperialism? Another reply to Claudio Katz on the actuality of the Marxist imperialism theory, 16 November 2024, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/are-we-living-in-the-age-of-empire-or-of-imperialism-3rd-reply-to-claudio-katz/
[2] Promise Li: Imperialism as Antagonistic Cooperation, 15 October 2024, https://spectrejournal.com/imperialism-as-antagonistic-cooperation/; https://links.org.au/imperialism-antagonistic-cooperation. All quotes are from this essay if not indicated otherwise.
[3] My most detailed works on the Marxist theory of imperialism are two books: Anti-Imperialism in the Age of Great Power Rivalry. The Factors behind the Accelerating Rivalry between the U.S., China, Russia, EU and Japan. A Critique of the Left’s Analysis and an Outline of the Marxist Perspective, RCIT Books, Vienna 2019, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/anti-imperialism-in-the-age-of-great-power-rivalry/; The Great Robbery of the South. Continuity and Changes in the Super-Exploitation of the Semi-Colonial World by Monopoly Capital Consequences for the Marxist Theory of Imperialism, RCIT Books, 2013, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/great-robbery-of-the-south/
[4] Promise Li: US-China rivalry, ‘antagonistic cooperation’ and anti-imperialism in the 21st century, 14 September, 2023, https://links.org.au/us-china-rivalry-antagonistic-cooperation-and-anti-imperialism-21st-century
[5] For a critique of the “sub-imperialism” theory see e.g. my essay: Semi-Colonial Intermediate Powers and the Theory of Sub-Imperialism. A contribution to an ongoing debate amongst Marxists and a proposal to tackle a theoretical problem, 1 August 2019, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/semi-colonial-intermediate-powers-and-the-theory-of-sub-imperialism/; see also chapter IV (“The Marxist Criteria for an Imperialist Great Power“ in our above-mentioned book “Anti-Imperialism in the Age of Great Power Rivalry”)
[6] Useful biographies of Bukharin are e.g. Stephen Cohen: Bukharin and the Bolshevik Revolution. A Political Biography, 1888–1938. Oxford University Press, 1980; Wladislaw Hedeler: Nikolai Bucharin. Stalins tragischer Opponent. Eine politische Biographie. Matthes & Seitz, Berlin 2015; Adolf G. Löwy: Die Weltgeschichte ist das Weltgericht. Leben und Werk Nikolai Bucharins. Promedia-Verlags-Gesellschaft, Wien 1990; Anna Larina: This I cannot forget. The Memoirs of Nikolai Bukharin's Widow. W. W. Norton & Co, New York 1993.
[7] On the history of the Right Opposition in English-language see e.g. Robert J. Alexander: The Right Opposition. The Lovestoneites and the International Communist Opposition of the 1930s, Greenwood Press, London 1981
[8] August Thalheimer: Grundlinien und Grundbegriffe der Weltpolitik nach dem 2. Weltkrieg, Gruppe Arbeiterpolitik, 1946, p. 11 and 9 (our translation)
[9] Nikolai Bukharin: Imperialism and World Economy (1915), International Publishers, New York 1929, p. 104
[10] Nikolai Bukharin: The Politics and Economics of the Transition Period (1920), Routledge, Abingdon 2003, pp. 63-64
[11] Nikolai Bukharin: Imperialism and World Economy, p. 148
[12] Ibid., p. 54
[13] On Alexander Bogdanov see e.g. James D. White: Red Hamlet: The Life and Ideas of Alexander Bogdanov, Brill, Leiden 2018; Dietrich Grille: Lenins Rivale: Bogdanov und seine Philosophie, Verlag Wissenschaft und Politik, Cologne 1966; see also the foreword of Bogdanov's Tektology Vol. 1 by Vadim N. Sadovsky and Vladimir V. Kelle, Centre for Systems Studies, University of Hull, 1996, pp. iii-xxii; V.A. Bazarov: Bogdanov as a Thinker, in: Alexander Bogdanov: Empiriomonism. Essays in Philosophy, Books 1–3, Brill, Leiden 2020, pp. xvii-xli.
[14] Nikolai Bukharin: Historical Materialism. A System of Sociology (1921), Authorized Translation from the third Russian edition, George Allen & Unwin, Ltd, London 1926, p. 74
[15] V.I. Lenin: On the Question of Dialectics (1915); in: CW 38, p.358
[16] Nikolai Bukharin: Historical Materialism, p. 79
[17] Ibid., p. 74
[18] Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel: Science of Logic, George Allen & Unwin, Ltd, New York 1969, p. 439 (also quoted in V.I. Lenin: Conspectus of Hegel’s Book the Science of Logic (1914); in: LCW 38, pp. 178-179)
[19] Friedrich Engels: Anti-Dühring. Herr Eugen Dühring's Revolution in Science, in: MECW Vol. 25, pp. 55-56
[20] V.I. Lenin: On the Question of Dialectics (1915); in: LCW 38, p.358
[21] Friedrich Engels: Dialectics of Nature, in: MECW Vol. 25, pp. 525-526
[22] Abram Deborin: Lenin als revolutionärer Dialektiker (1925); in: Nikolai Bucharin, Abram Deborin: Kontroversen über dialektischen und mechanistischen Materialismus, Frankfurt a.M. 1974, p. 54 (our translation)
[23] N.A. Karew: Die Theorie des Gleichgewichts und der Marxismus; in: Wilhelm Goerdt (Hrsg.): Die Sowjetphilosophie. Wendigkeit und Bestimmtheit. Dokumente, Darmstadt 1967, p. 139 (our translation)
[24] Ibid., pp. 140-141
[25] Abram Deborin: Lenin als revolutionärer Dialektiker (1925); in: Unter dem Banner des Marxismus, 1. Jahrgang (1925-26), p. 224 (our translation)
[26] Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel: The Science of Logic, (Translated by A.V. Miller), Humanity Books, New York 1969, p. 826
[27] Leon Trotsky: The capitalist curve of development (1923), in: Leon Trotsky: Problems of Everyday Life, New York, 1994, pp. 273-280
[28] For our analysis of the current historic period see e.g. chapter 14 in the above-mentioned book “The Great Robbery of the South” as well as chapter I and II in the above-mentioned book “Anti-Imperialism in the Age of Great Power Rivalry”.
[29] See e.g. RCIT: Theses on Agriculture and Ecology, September 2023, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/theses-on-agriculture-and-ecology/, Almedina Gunić: The Deadly Breath of Imperialism, 23.10.2017, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/pollution-caused-the-death-of-9-million-people-in-2015/
[30] Murray E.G. Smith, Josh Watterton: Valorization, Financialization & Crisis: A Temporal Value-Theoretic Approach, 2021, p. 5
[31] M. Ayhan Kose, Franziska Ohnsorge (Eds.): A Decade since the Global Recession, Lessons and Challenges for Emerging and Developing Economies, World Bank, 2019, p. 9
[32] Karl Marx: Economic Manuscripts of 1861-63. Capital and Profit. 7) General Law of the Fall in the Rate of Profit with the Progress of Capitalist Production; in: MECW, Volume 33, pp. 104-145; http://www.marxists.org/archive/marx/works/1861/economic/ch57.htm
[33] Michael Roberts: Has globalisation ended? (2022), https://thenextrecession.wordpress.com/2022/04/27/has-globalisation-ended/
[34] I have published a number of works about capitalism in China and its rise to an imperialist power. The most important ones are the following: Chinese Imperialism and the World Economy, an essay published in the second edition of “The Palgrave Encyclopedia of Imperialism and Anti-Imperialism” (edited by Immanuel Ness and Zak Cope), Palgrave Macmillan, Cham, 2020, https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007%2F978-3-319-91206-6_179-1; China: On the Relationship between the “Communist” Party and the Capitalists. Notes on the specific class character of China’s ruling bureaucracy and its transformation in the past decades, 8 September 2024, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/china-on-the-relationship-between-communist-party-and-capitalists/; China: On Stalinism, Capitalist Restoration and the Marxist State Theory. Notes on the transformation of social property relations under one and the same party regime, 15 September 2024, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/china-on-stalinism-capitalist-restoration-and-marxist-state-theory/; China: An Imperialist Power … Or Not Yet? A Theoretical Question with Very Practical Consequences! Continuing the Debate with Esteban Mercatante and the PTS/FT on China’s class character and consequences for the revolutionary strategy, 22 January 2022, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/china-imperialist-power-or-not-yet/; China‘s transformation into an imperialist power. A study of the economic, political and military aspects of China as a Great Power (2012), in: Revolutionary Communism No. 4, https://www.thecommunists.net/publications/revcom-1-10/#anker_4; How is it possible that some Marxists still Doubt that China has Become Capitalist? An analysis of the capitalist character of China’s State-Owned Enterprises and its political consequences, 18 September 2020, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/pts-ft-and-chinese-imperialism-2/; Unable to See the Wood for the Trees. Eclectic empiricism and the failure of the PTS/FT to recognize the imperialist character of China, 13 August 2020, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/pts-ft-and-chinese-imperialism/; China’s Emergence as an Imperialist Power (Article in the US journal 'New Politics'), in: “New Politics”, Summer 2014 (Vol:XV-1, Whole #: 57). See many more RCIT documents at a special sub-page on the RCIT’s website: https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/china-russia-as-imperialist-powers/.
[35] Figures for the year 2000: APEC: Regional Trends Analysis, May 2021, p. 2; the figures for Germany and India in the first column are for the year 2005 (UNIDO: Industrial Development Report 2011, p. 194); figures for the year 2022: UNIDO: International Yearbook of Industrial Statistics Edition 2023, pp. 36-37
[36] Fortune Global 500, August 2023, https://fortune.com/ranking/global500/2023/ (the figures for the share is our calculation)
[37] Forbes: Forbes Billionaires 2023, https://www.forbes.com/sites/chasewithorn/2023/04/04/forbes-37th-annual-worlds-billionaires-list-facts-and-figures-2023/?sh=23927e7477d7
[38] Hurun Global Rich List 2024, 26.03.2024, https://www.hurun.net/en-US/Info/Detail?num=K851WM942LBU
[39] See e.g. Michael Pröbsting: Russia Overtakes Japan to Become Fourth Largest Economy in the World, 5 July 2024, https://www.thecommunists.net/worldwide/global/russia-overtakes-japan-to-become-fourth-largest-economy-in-the-world/
[40] I have published a number of works about capitalism in Russia and its rise to an imperialist power. The most important ones are the following pamphlets: The Peculiar Features of Russian Imperialism. A Study of Russia’s Monopolies, Capital Export and Super-Exploitation in the Light of Marxist Theory, 10 August 2021, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/the-peculiar-features-of-russian-imperialism/; Lenin’s Theory of Imperialism and the Rise of Russia as a Great Power. On the Understanding and Misunderstanding of Today’s Inter-Imperialist Rivalry in the Light of Lenin’s Theory of Imperialism. Another Reply to Our Critics Who Deny Russia’s Imperialist Character, August 2014, http://www.thecommunists.net/theory/imperialism-theory-and-russia/; Russia as a Great Imperialist Power. The formation of Russian Monopoly Capital and its Empire, 18 March 2014, http://www.thecommunists.net/theory/imperialist-russia/.
[41] SIPRI Yearbook 2024: Armaments, Disarmament and International Security, p. 272
[42] Nan Tian, Diego Lopes Da Silva, Xiao Liang and Lorenzo Scarazzato: Trends in World Military Expenditure, SIPRI, 2023, p. 2
[43] See on this: Henry Meyer, S'thembile Cele, and Simone Iglesias: Putin Hosts BRICS Leaders, Showing He Is Far From Isolated, Bloomberg, 22 October 2024, https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2024-10-22/putin-hosts-brics-leaders-in-russia-defying-attempts-from-west-to-isolate-him; Dr Kalim Siddiqui: The BRICS Expansion and the End of Western Economic and Geopolitical Dominance, 30 October 2024, https://worldfinancialreview.com/the-brics-expansion-and-the-end-of-western-economic-and-geopolitical-dominance/; Walid Abuhelal: Can the Brics end US hegemony in the Middle East? Middle East Eye, 22 October 2024 https://www.middleeasteye.net/opinion/can-brics-end-us-hegemony-middle-east; Anthoni van Nieuwkerk: BRICS+ wants new world order sans shared values or identity, 30 October 2024 https://asiatimes.com/2024/10/brics-wants-new-world-order-sans-shared-values-or-identity/
[44] Ben Aris: Can the BRICS beat the G7? Intellinews, 19 October 2024, https://www.intellinews.com/can-the-brics-beat-the-g7-348632/?source=south-africa
[45] Nan Tian et al: Trends in World Military Expenditure, p. 2
[46] World Bank: Merchandise trade (% of GDP), accessed on 21 November 2024, https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/TG.VAL.TOTL.GD.ZS?view=chart
[47] See on this e.g. Helga Nussbaum: Der europäische Wirtschaftsraum. Verflechtung, Angleichung, Diskrepanz, in: Fritz Klein, Karl Otmar von Aretin (Eds): Europea um 1900, Akademie-Verlag, Berlin 1989, p. 49
[48] Stefano Battilossi: The Determinants of Multinational Banking during the First Globalization, 1870-1914, Working Papers 114, Oesterreichische Nationalbank (Austrian Central Bank), 2006, p. 40
Emperyalizm: Bir "Antagonistik İşbirliği" Sistemi mi Yoksa Antagonistik Çelişkiler Sistemi mi?
Promise Li'nin Marksist emperyalizm teorisine yaptığı bir katkıya yanıt
Bir Deneme (8 Tablo ve 2 Şekil ile) Michael Pröbsting, 23 Kasım 2024
Bu çeviri Köstebek Kolektif tarafından yapılmıştır.
İÇİNDEKİLER
Giriş
Li'nin "antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramının kısa bir özeti
Thalheimer ve Buharin gerçekten de "antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramının öncüleri miydi?
Kusurlu bir metodolojik temel: Buharin'in diyalektik olmayan denge teorisi
Materyalist diyalektik açısından bir eleştiri
21. yüzyılda kapitalizm: büyüme dinamiğini geri kazanmak mı?
Çin ve Rus emperyalizminin yükselişini abartıyor muyuz?
Kapitalist karşılıklı bağımlılık emperyalistler arası savaş için bir engel midir?
Sonuçlar
Giriş
Geçenlerde Arjantinli iktisatçı Claudio Katz'a verdiğim bir yanıtta da belirttiğim gibi, Marksistler arasında emperyalizm teorisine ilişkin tartışmalar son birkaç yılda yoğunlaştı. [1] Birkaç hafta önce bir başka sosyalist yazar, Promise Li, bu tartışmaya bir katkı daha yayınladı. [2]
Hong Konglu bir sosyalist olan Promise Li, şu anda Los Angeles'ta yaşamakta ve Tempest Collective ve Solidarity (ABD) üyesi olarak faaliyet göstermektedir. Katkısı, bir yandan "ABD İmparatorluğu"nu tek ve biricik emperyalist güç olarak görenlerden, diğer yandan da Lenin'in ortodoks emperyalizm teorisini destekleyenlerden ayırdığı "antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramının detaylandırılmasıdır. Benden (doğru bir şekilde) ikinci kampın destekçisi olarak bahsettiği için, eleştirisine yanıt vermek istiyorum. Hem metodolojik hem de ampirik olarak, "antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramının mevcut dönemdeki dünya durumunun dinamiklerini anlamaya izin vermediğini göstereceğim.
Bu geniş bir konu olduğundan, kendimi Li tarafından sunulan spesifik argümanlar ve eleştirilerle sınırlamaya çalışacağım. Marksist emperyalizm teorisine ilişkin anlayışımı daha kapsamlı bir şekilde açıklamak için okuyucuları önceki çalışmalarıma yönlendiriyorum. [3]
Li'nin "antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramının kısa bir özeti
İlk olarak, Promise Li'nin, tartışmaya katkıda bulunan diğer birçok kişinin aksine, Çin emperyalizmiyle herhangi bir uzlaşmayı sürekli olarak reddettiğini belirtmek isterim. Bir röportajında belirttiği gibi, "sol, ABD ve Çin emperyalizmlerine karşı direnenler arasında bağlar kurmaya odaklanmalıdır." [4] Dolayısıyla, kendisini Washington'un suçlarını şiddetle kınayan ancak Pekin ve Moskova'nın suçları söz konusu olduğunda çok kısıtlı kalan tek gözlü bir anti-emperyalizme bağlı olan (proto-)Stalinist yazarlardan olumlu bir şekilde ayırmaktadır. Şüphesiz Li'nin Hongkong'daki Xi rejiminin acımasız gerçekliğine dair ilk elden deneyimi, anlayışına oldukça yardımcı olmuştur.
Bununla birlikte, emperyalistler arası rekabeti küçümsediği ve Büyük Güçler arasındaki istikrar ve işbirliğini abarttığı için emperyalizm kavramı sorunludur. Buna karşılık ben kapitalist dünya sistemini uzun vadeli bir gerileme içinde olan bir sistem olarak görüyorum. Böyle bir dönemde, Batı ve Doğu'daki emperyalist güçler (ABD, Batı Avrupa, Japonya, Çin ve Rusya) arasındaki ve bu güçler ile yarı-sömürge ülkeler arasındaki çelişkilerin şiddetlenmesi kaçınılmazdır. Emperyalizm "antagonistikişbirliği" ile değil, daha ziyade antagonistik çelişkilerle karakterize edilen bir sistemdir.
"Antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramının kusurlarını tartışmadan önce, Li'nin sunumunun bir özetiyle başlayacağız. Li, teorisinin kökenlerini Alman komünist August Thalheimer ve önde gelen Bolşevik teorisyenlerden Nikolai Bukharin'in yazılarına dayandırmaktadır. "Antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramı daha sonra Brezilyalı Marksist kolektif Política Operária (POLOP) tarafından yeniden ele alınmış ve bu kolektifin üyeleri arasında alt-emperyalizm teorisiyle tanınan Ruy Mauro Marini de yer almıştır.
Alt-emperyalizm teorisinin, "antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramı gibi, diyalektik bir yaklaşımdan yoksun olduğunu belirtmek isteriz. Ancak bu noktada bu konuyu tartışmayacak ve okuyucuları alt-emperyalizm teorisini ele aldığımız diğer çalışmalara yönlendireceğiz. [5]
Bu metodolojik temelden yola çıkan Promise Li, bu kavramı günümüz emperyalist dünya düzenini analiz etmek için kullanmaktadır. "Thalheimer'ın tanımını değiştirebilir ve antagonistik işbirliğini, farklı eğilimler olarak işbirliği ve rekabetten ziyade, ulusal sermayeler arasındaki rekabet koşullarının "karşılıklı emperyal çıkarların ve alanların iç içe geçmesi" yoluyla şekillendiği ya da buna aracılık ettiği emperyalizmin belirli bir aşaması olarak düşünebiliriz."
Bununla bağlantılı olarak yazar, kapitalist dünya sisteminin göreli istikrarını vurgulamaktadır. Elbette tekrarlanan krizlerin farkındadır, ancak güçler arasında işbirliği eğiliminin hakim olduğunu düşünmektedir.
"Bu analiz, devletler arasında her zaman var olan düşmanca kriz ve rekabet tehdidini küçümsemeden, emperyalist dünya sisteminin küresel birikim yollarını en üst düzeye çıkarmak için işbirliği dinamiklerini sürdürme kapasitesini ön plana çıkarmaktadır."
Sonuç olarak Li, kendi kavramını bir yandan "ABD liderliğindeki bir İmparatorluğun" dünyaya hakim olacağı gibi diğer teorilerden, diğer yandan da ortodoks Marksist emperyalizm teorisinden ayırmaktadır.
"[K]apitalizmin iyileşme ve istikrar için yeni terimler geliştirmek üzere kendi yapısını yeniden düzenlemesini gözden kaçırmamalıyız. Savaş sonrası Almanya ve Brezilya'da Marksistler tarafından geliştirilen kavramsal bir çerçeve olan antagonistik işbirliği, emperyalizmin bu özel aşamasını analiz etmek için en iyi araçları sağlamaktadır. Her ikisi de emperyalist güçler arasındaki rekabete aşırı vurgu yapan Tricontinental'in tek kutuplu kuramsallaştırmasının ya da Bolşevik kuramcıları izleyenlerin çok kutuplu rekabetinin aksine, antagonistik işbirliği emperyalist sistemi jeopolitik bloklar arasında ve ötesinde karşılıklı bağımlılığı barındırabilen birbirine bağımlı bir bütünlük olarak anlar. Ayrıca, yukarıda açıklanan iki modelden farklı olarak, antagonistik işbirliği, merkez ve çevre ekonomileri arasındaki genel bağımlılık yapısı varlığını sürdürse bile, bu paradigma içinde güç ilişkilerinin heterojenliğine de izin vermektedir. Birincisi, Amerika Birleşik Devletleri ve Çin arasındaki rekabet, hala birincisinin liderliğinde ve hakimiyetinde olan küresel emperyalist sistemde eşit oldukları anlamına gelmemektedir. Claudio Katz'ın "oluşum halindeki imparatorluklar" olarak adlandırdığı diğer ara veya alt emperyal ülkeler de zaman zaman ABD'nin gücünü askeri, ekonomik veya diğer yollarla kontrol etme becerisini geliştirmektedir. Ancak bu durum ne ABD hegemonyasına karşı anti-emperyalist bir saldırıya ne de emperyalistler arası rekabetin yeni bir alanı olarak oyun alanının doğrudan düzleşmesine işaret ediyor."
"Ekonomik karşılıklı bağımlılık, rakip jeopolitik bloklar arasında bile şaşırtıcı bir esneklik göstermiştir. Mevcut emperyalizm teorileri, günümüz dünya sisteminin görünüşte çelişkili olan bu boyutlarını tam olarak açıklayamamaktadır. Tricontinental, emperyalizmin mevcut aşamasını, diğer tüm küresel çelişkileri ikincil veya "antagonistik olmayan" hale getiren tek emperyalist güç olarak tek kutuplu "ABD Liderliğindeki Askeri Blok" ile karakterize edilen "hiper-emperyalizm" olarak teorize etmektedir. Tricontinental yazarlarına göre bu emperyalist bloğa, "Küresel Güney'den yükselen ulusal egemenlik, ekonomik modernleşme ve çok taraflılık için artan istekleri" temsil eden çok kutuplu "Çin liderliğindeki sosyalist gruplaşma" tarafından meydan okunmaktadır. Böyle bir bakış açısı, hem iki blok arasındaki karşılıklı bağımlılığın hem de bazı ara ekonomilerin (örneğin İran, Birleşik Arap Emirlikleri ve Rusya) jeopolitik gerilimlerin ortasında emperyalizmi kolaylaştıran bölgesel hegemonyalar geliştirmedeki rolünün sonuçlarını göz ardı etmektedir.
Tricontinental'in aksine, bazıları bugünkü emperyalizm biçimini, Bolşevik devrimciler V. I. Lenin ve Nikolai Bukharin'in ilk kez teorize ettiği Birinci Dünya Savaşı'na benzer bir ara-emperyalist çatışma olarak görmektedir. Bu görüş, ABD hegemonyasının gerilemesini aşırı derecede küçümserken, ABD emperyalizmine karşı bir denge unsuru olarak yeni emperyalistlerin yükselişini abartmaktadır. Bu hatalı anlayışlar aynı madalyonun iki yüzü gibidir: rekabet dinamiklerini abartırlar ve böylece emperyalist sistemde sistem karşıtı mücadeleler arasında dayanışma için güçlü fırsatlar yaratabilecek belirgin bağlantı alanlarını gizlerler."
Thalheimer ve Buharin gerçekten de "antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramının öncüleri miydi?
Buharin ve Thalheimer kimlerdi? Buharin genç ve adanmış bir militan olarak Bolşeviklere katıldı ve sürgündeki diğer Rus devrimcilere katılmadan önce Moskova yeraltı partisinde çalıştı. 1917'de Bolşevik lider oldu ve devrimden sonraki ilk on yılda partinin politikasını şekillendirmede kilit bir figürdü. Buharin, emperyalizm teorisi, devlet teorisi ve ulusal sorun gibi konularda Lenin ile defalarca çatışan yetenekli bir teorisyendi. Bununla birlikte, düşünceli ve ilham verici bir Marksist entelektüeldi ve Lenin onun çalışmalarını takdir ediyor, hatta onu " partinin sevgilisi" olarak adlandırıyordu.
Buharin başlangıçta partideki aşırı sol kanadın sözcüsü iken, 1923'te Stalin'in fraksiyonuna katıldı ve Komintern'in oportünist stratejisinin, rejimin Kulak yanlısı politikasının ve Leon Troçki liderliğindeki Sol Muhalefet 'in ihraç edilmesinin teorileştirilmesinde önemli bir rol oynadı. Ancak, 1927 sonlarında otantik Bolşeviklerin bastırılmasından kısa bir süre sonra, geçmişteki Kulak yanlısı politikalarının bir sonucu olarak ekonomik krizle karşı karşıya kalan Stalinist bürokrasi, köylülüğün zorla kolektifleştirilmesine ve süper sanayileşmeye yöneldi. Sonuç olarak, Buharin'in artık "yenibirCengiz Han" olduğunu fark ettiği Stalin, eski "partinin sevgilisini" de kovdu. Ancak, Troçkistlerin aksine, Buharin ve destekçileri bir muhalefet mücadelesi başlatmaktan kaçındılar ve hızla Stalin'e teslim oldular. Bu, Buharin'in bağımsız bir politikacı olarak sonu oldu ve birkaç yıl sonra, 1936-38'deki korkunç gösteri duruşmaları sırasında hepsi kurşuna dizildi. [6]
August Thalheimer 1914'ten önce Alman sosyal demokrasisinin sol kanadının bir parçasıydı ve I. Dünya Savaşı sırasında Rosa Luxemburg ve Karl Liebknecht'in Spartaküs Birliği'ne katıldı. 1921'de Heinrich Brandler ile birlikte Komünist Parti'nin liderliğini üstlendiğinde partinin önde gelen teorisyeni oldu. Ancak, 1923'ün ikinci yarısındaki devrimci durumda ("Alman Ekim'i" gerçekleşmedi) sefil bir şekilde başarısız olduklarından, liderlik görevlerinden çekilmek zorunda kaldılar. Entelektüel akıl hocaları Buharin'in 1928'de düşüşünden sonra Brandler ve Thalheimer, Stalinistleri yalnızca aşırı sol (ama oportünist değil) hataları nedeniyle eleştiren ve rejime karşı muhalif bir mücadele çağrısında bulunmayan sözde uluslararası Sağ Muhalefeti kurdular. Daha da kötüsü, 1930'ların ortalarında baş oportünist halk cephesi politikasını tamamen desteklediler ve Moskova'daki göstermelik duruşmaları kınamayı reddettiler. Şaşırtıcı olmayan bir şekilde, uluslararası Sağ Muhalefet 1930'ların sonunda dağıldı ve İkinci Dünya Savaşı'ndan sonra Almanya'da sadece küçük bir grup varlığını sürdürdü. [7]
Metodolojik başarısızlıklarına rağmen Buharin ve Thalheimer - ilki ikincisinden çok daha fazla - bir dizi düşünceli katkıda bulunmuş ciddi teorisyenlerdi.
Promise Li ve POLOP kolektifi "antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramını Thalheimer'in Almanca bir broşürüne dayandırmaktadır: "Grundlinien und Grundbegriffe der Weltpolitik nach dem 2. Dünya Savaşı Sonrası Dünya Politikasının Temel İlkeleri ve Kavramları" başlıklı, 1946 yılında yayınladığıbroşürüne dayanmaktadır. Bu broşürde Alman komünist, ABD'nin başını çektiği emperyalist ittifakı "antagonistik işbirliği" olarak adlandırmıştır.
Ancak bu terimin Thalheimer'in broşüründen kaynaklandığı doğru olmakla birlikte, POLOP'un ve Li'nin bu belgeye atıfta bulunması son derece sorunludur. Alman komünist bu çalışmasında "antagonistik işbirliği" terimini İkinci Dünya Savaşı sonrasındaki durumun bir tanımı olarak görmüştür. Ancak emperyalist güçler arasındaki işbirliğinin a) Batılı güçler ile genişleyen Stalinist kamp arasındaki ağır basan sınıf çelişkilerine ve b) ABD'nin mutlak üstünlüğüne dayandığını kabul ediyordu.
Sonuç olarak, Thalheimer'ın dünya düzenine bakışı "işbirliği" değil, emperyalist ittifakın Stalinist kampa, yani yozlaşmış işçi devletlerine karşı kolektif saldırganlığa dayanması nedeniyle yaklaşmakta olan III.
"Emperyalistlerin bölgesel genişleme dürtüsünün kapitalist kamp içinde savaşla değil, daha ziyade farklı derecelerde emperyalist işbirliğiyle sonuçlanmasına neden olan faktörleri gösterdik. Dolayısıyla, bu bölgesel genişleme dürtüsü yalnızca dışarıya yöneltilebilir: sosyalist sektöre, Sovyetler Birliği'ne ve onun etki alanına karşı."
"Bu gerçekler bir şey gösteriyorsa, o da İkinci Dünya Savaşı'nın hemen ardından yeni bir dünya savaşı için devam eden genel konuşlanmadır." [8]
Bununla birlikte, Promise Li'nin emperyalizm kavramını "düşmanca işbirliği" olarak anlaması farklı bir anlayıştır. SSCB ve müttefikleri otuz yıldır var olmadığından, böyle bir işbirliği artık ortak bir düşmana karşı ortak bir saldırı politikasına dayanamaz. Dolayısıyla Li, "antagonistik işbirliğini" emperyalizmin yeni bir aşaması olarak görmektedir - emperyalist güçleri bir arada tutacak ortak bir düşmanın varlığından bağımsız olarak (1945-91 yılları arasında SSCB liderliğindeki Stalinist kamp gibi). Buna karşılık Thalheimer, "antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramını, İkinci Dünya Savaşı'nın sonuçlarının kendine has özelliklerinden kaynaklanan özel bir durumun konjonktürel bir açıklaması olarak detaylandırdı. Alman komünistine göre, ortak düşman ortadan kalktığında böyle bir "antagonistikişbirliği" durumu artık var olmayacaktı.
Aynı şekilde, Buharin'in kendine özgü emperyalizm analizi de, kesinlikle hatasız değildir, Li'nin savunduğu gibi "antagonistikişbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramına yaklaşan bir yaklaşıma sahip değildir. Nispeten istikrarlı bir dünya ve hatta Büyük Güçler arasında hakim bir işbirliği varsaymak bir yana, emperyalizmi daha ziyade emperyalistler arası keskin rekabet ve bunlar arasında savaş eğilimi ile karakterize edilen antagonistik bir sistem olarak görüyordu.
"Toplumun egemen çevreleri açısından, burjuvazinin "ulusal" grupları arasında kaçınılmaz olarak günümüz toplumunun içinde ortaya çıkan sürtüşmeler ve çatışmalar, daha da gelişerek sorunun tek çözümü olarak savaşa yol açar. Bu sürtüşme ve çatışmaların dünya sermayesinin yeniden üretim koşullarında meydana gelen değişikliklerden kaynaklandığını gördük. Bir dizi karşıt unsur üzerine inşa edilmiş olan kapitalist toplum, ancak acı krizler pahasına göreli bir denge sağlayabilir." [9]
"Finans kapitalizmi sistemine geçiş, basit piyasa, yatay rekabetin karmaşık rekabete dönüştüğü süreci sürekli olarak güçlendirdi. Mücadele yöntemi rekabet türüne tekabül ettiğinden, bunu kaçınılmaz olarak dünya pazarındaki ilişkilerin 'şiddetlenmesi' izlemiştir. Doğrudan baskı yöntemleri dikey ve yatay rekabete eşlik eder, bu nedenle dünya finans kapital sistemi kaçınılmaz olarak emperyalist rakipler arasında silahlı bir mücadeleyi içerir. Emperyalizmin temel kökleri de burada yatmaktadır. (...) Üretici güçlerin gelişimi ile kapitalist üretim ilişkileri arasındaki çatışma - tüm sistem havaya uçmadığı sürece - üretici güçleri geçici olarak azaltmalıdır, böylece gelişimlerinin bir sonraki döngüsü aynı kapitalist kabuk içinde başlayabilir. Üretici güçlerin bu yıkımı kapitalist gelişmenin olmazsa olmaz koşulunu oluşturur ve bu açıdan bakıldığında krizler, rekabetin maliyetleri ve - bu maliyetlerin özel bir örneği olan - savaşlar kapitalist yeniden üretimin kaçınılmaz faux frais'leridir." [10]
Gördüğümüz gibi Buharin -Li'nin aksine- kapitalist üretim ve yeniden üretimin uluslararasılaşmasını emperyalistler arası gerilimleri sınırlayacak bir özellik olarak görmüyordu. Daha ziyade bunu Büyük Güçler arasındaki çatışmaları hızlandıracak bir gelişme olarak görüyordu.
"Uluslararası işbölümü, doğal ve toplumsal koşullardaki farklılık, Dünya Savaşı ile bile yok edilemeyecek bir ekonomik önceliğe sahiptir. Böyle olduğu için, belirli değer ilişkileri ve bunların sonucu olarak, uluslararası işlemlerde azami kârın gerçekleştirilmesi için koşullar vardır. Ekonomik açıdan kendi kendine yeterlilik değil ama uluslararası ilişkilerin yoğunlaşması ve buna eş zamanlı olarak "ulusal" konsolidasyon ve dünya rekabeti temelinde yeni çatışmaların olgunlaşması eşlik etmektedir; gelecekteki evrimin yolu budur." [11]
Bu nedenle Bolşevik teorisyen savaşı emperyalizmin "içkinbiryasası" olarak nitelendirmiştir: "Kapitalist toplumda savaş, dünya ekonomisi alanına yayıldığında, kapitalist rekabetin yöntemlerinden yalnızca biridir. Bu nedenle savaş, kendiliğinden gelişen bir dünya pazarının kör yasalarının baskısı altında mal üreten bir toplumun içkin bir yasasıdır, ancak üretim ve dağıtım sürecini bilinçli olarak düzenleyen bir toplumun yasası olamaz." [12]
Özetle, Li'nin POLOP'un Thalheimer ve Buharin'e "antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramının öncüleri olarak atıfta bulunmasının gerekçeden yoksun olduğunu düşünüyoruz.
Kusurlu bir metodolojik temel: Buharin'in diyalektik olmayan denge teorisi
Bunu söyledikten sonra, Li'nin Buharin ve Thalheimer'in yazılarına işaret etmesinde de bir haklılık payı olduğunu inkar etmiyoruz. Bunun nedeni, "antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramının bu iki teorisyenle düşünce tarzlarında belirli metodolojik benzerlikler paylaşmasıdır. Yani, hepsi de - bilinçli ya da bilinçsiz - diyalektikten yoksun mekanist denge teorisini benimsemektedir.
Yukarıda alıntılandığı üzere, Li'nin "analizi, emperyalist dünya sisteminin küresel birikim yollarını maksimize etmek için işbirlikçi dinamikleri sürdürme kapasitesini ön plana çıkarmaktadır." Aynı şekilde, başka bir yazarın "sistemin devamı için [emperyalistler arasında] işbirliğinin hüküm sürdüğünü" söylediğini onaylayarak aktarıyor:
"Sachs'ın yazdığı gibi: 'Antagonistik işbirliği kapitalist dünyayı her düzeyde, iniş ve çıkışlarda iç şoklardan kurtarmaz. Ulusal burjuvaziler "bağımsız" bir dış politika tehdidinde bulunduğunda, Uluslararası Para Fonu'nun planlarına karşı isyan ettiğinde ve özellikle popüler olmayan yabancı şirketleri kamulaştırdığında, antagonizmanın baskın göründüğü anlar vardır. Aynı olgu, uluslararası gerilimin periyodik olarak gevşediği anlarda emperyalist güçlerin kendi aralarında da ortaya çıkar. Uluslararası gerilimde yeni bir yükseliş olduğunda ve 1968'de Fransa'da olduğu gibi kapitalist rejim kontrol altına alındığında ortadan kaybolur. Uzun vadede sistemin devamı için işbirliği hakim olur."
Daha önce de belirtildiği gibi, Buharin emperyalist dünyanın bir işbirliği dünyası olduğu görüşüne katılmamakla birlikte, diyalektik materyalizme karşı çıkan ve "örgütsel felsefe" adı verilen bir sistem geliştiren Alexander Bogdanov'un felsefi öğretilerine sempati duyuyordu. Bogdanov 1904-08 yıllarında Bolşevikler arasında önde gelen bir figürdü, ancak siyasi farklılıklar - 1905-07'deki ilk Rus Devrimi'nin yenilgisinden sonra idealist felsefesini aşırı sol politikalara destekle birleştirdi - partiyi felç etme tehdidinde bulunduğunda Lenin ona ve felsefesine karşı şiddetli bir mücadele yürütmek zorunda kaldı. Lenin'in ünlü felsefi çalışması "Materyalizm ve Ampirio-eleştiri" temelde Bogdanov'un hem materyalizmden hem de diyalektikten yoksun felsefesine karşı birpolemiktir. [13]
Buharin - Lenin'in vasiyetinde "diyalektik üzerine hiç çalışmadı ve sanırım onu hiçbir zaman tam olarak takdiretmedi" dediği - Bogdanov'un denge teorisini benimsedi. Bu teori temelde gerçekliği, tekrar tekrar ani krizlerle bozulan ve bir süre sonra yeni bir denge olarak yeniden istikrara kavuşan (göreceli, hareketli) bir denge olarak görür. Başka bir deyişle, denge şeylerin doğal konumu olacaktır. Buharin, "Tarihsel Materyalizm" adlı kitabında böyle bir görüşü açıkça ifade eder.
"Öte yandan, burada bu sürecin biçimine de sahibiz: ilk olarak, denge durumu; ikinci olarak, bu dengenin bozulması; üçüncü olarak, dengenin yeni bir temelde yeniden kurulması. Ve sonra hikaye yeniden başlar: yeni denge yeni bir kargaşanın çıkış noktasıdır, bu kargaşayı da başka bir denge durumu takip eder, vs. sonsuza kadar gider." [14]
Bu, Buharin'in çelişkileri ve bunun sonucunda ortaya çıkan hareketi gelişimin önemli itici güçleri olarak görmezden geldiği anlamına gelmez. Bununla birlikte, çelişkileri her şeyin (denge de dahil olmak üzere) içsel, temel bir özelliği olarak değil, daha ziyade dışsal bir şey olarak görüyordu. Bunun nedeni, maddeyi ve hareketini anlamak için temel yasa olarak zıtların birliğini ve çelişkili parçaları arasındaki mücadeleyi göz ardı etmesidir. Lenin'in dediği gibi "gelişme karşıtların "mücadelesi "dir". [15] Dolayısıyla Buharin için hareket iç çelişkilerden ziyade farklı şeyler (dengeler) arasındaki çelişkilerden kaynaklanıyordu.
Söz konusu kitapta böyle yazmıştır. "Eğer bir büyüme koşulunda toplumun yapısı fakirleşirse, yani içsel bozuklukları artarsa, bu yeni bir çelişkinin ortaya çıkmasına eşdeğer olacaktır: dışsal ve içsel denge arasındaki çelişki, eğer toplum büyümeye devam edecekse, bir yeniden yapılanmaya gitmesini, yani içsel yapısının kendisini dışsal dengenin karakterine uyarlamasını gerektirecektir. Sonuç olarak, iç (yapısal) denge, dış dengeye bağlı olan (bu dış dengenin bir "fonksiyonu" olan) bir niceliktir." [16]
"Kesin denge anlayışı yaklaşık olarak aşağıdaki gibidir: "Bir sistem için, sistem kendi kendine, yani kendisine dışarıdan enerji sağlanmadan, bu durumdan çıkamadığı zaman denge durumunda olduğunu söyleriz." [17]
Elbette Buharin iç çelişkilerin rolünü açıkça inkâr etmedi. Bunun için fazla zeki bir Marksist entelektüeldi. Ancak niyetine rağmen, hareketin birincil itici gücü olarak iç çelişkilerin belirleyici rolünü sistematik olarak hafife almıştır.
Materyalist diyalektik açısından bir eleştiri
Buharin'in mekanist denge teorisi ile "antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramı arasındaki bağlantı zaten açık hale gelmektedir. Karşıtların mücadelesini ve harekete neden olan iç çelişkileri küçümseyen felsefe, gerçekliğin (hareketli) bir denge durumu olarak anlaşılmasıyla sonuçlanır. Böylesi bir metodolojik temelde, dünya durumunu öncelikle göreli istikrar ve emperyalistler arasındaki işbirliği ile karakterize edilen bir durum olarak görmek kolaylaşır. Sonuç olarak, kafalar karışır ve dünya siyasetinin ve ekonomisinin hareket yönü fark edilemez.
Mekanist yöntem çok önemli bir soruyu doğru bir şekilde yanıtlamaktan acizdir: maddenin belirleyici özelliği nedir - denge ya da çelişki durumu, karşıtların mücadelesinin bir sonucu olarak hareket? Materyalist diyalektik açısından doğru cevap, karşıtların mücadelesinin, çelişkinin, harekete, dönüşüme, ilerlemeye neden olduğu için belirleyici özellik olduğudur. Buna karşılık, denge durumu yalnızca geçici bir andır. Hegel şunu söylerken kesinlikle haklıydı: "Çelişki tüm hareket ve canlılığın köküdür ve ancak bir Çelişki içerdiği ölçüde herhangi bir şey hareket eder, dürtü ve etkinliğe sahip olur." [18]
Bu aynı zamanda Marx ve Engels'in de anlayışıydı. Marx, "Anti-Dühring" adlı eserinde:
"Hareket maddenin varoluş biçimidir. Hiçbir yerde devinimsiz madde olmamıştır, olamaz da. Kozmik uzaydaki hareket, çeşitli gök cisimlerindeki daha küçük kütlelerin mekanik hareketi, ısı ya da elektrik veya manyetik akımlar olarak moleküllerin titreşimi, kimyasal parçalanma ve birleşme, organik yaşam - her bir anda dünyadaki her bir madde atomu bu hareket biçimlerinden birinde ya da diğerinde ya da aynı anda birkaç biçimdedir. Tüm dinlenme, tüm denge yalnızca görecelidir, yalnızca bir ya da diğer belirli hareket biçimiyle ilişkili olarak anlam kazanır. (...) Hareketsiz madde, maddesiz hareket kadar düşünülemez. Dolayısıyla hareket, maddenin kendisi kadar yaratılamaz ve yok edilemezdir." [19]
Bu yaklaşımdan hareketle Lenin, "Diyalektik Sorunu Üzerine" adlı makalesinde hareketin ve karşıtlar arasındaki mücadelenin mutlak, istikrarın, karşıtların birliğinin ise göreli olduğunu vurgulamıştır.
"Karşıtların birliği (çakışma, özdeşlik, eşit eylem) koşulludur, geçicidir, görecelidir. Birbirini dışlayan karşıtların mücadelesi mutlaktır, tıpkı gelişim ve hareketin mutlak olması gibi." [20]
Dolayısıyla materyalist diyalektik, dengeyi maddenin "normal" ya da "temel" koşulu olarak görmeyi reddeder. Bu daha ziyade uzun bir hareket sürecinin geçici bir aşamasıdır. Engels'in "Doğanın Diyalektiği" için yaptığı ön çalışmalarda belirttiği gibi:
"[B]ireysel hareket dengeye doğru çabalar, bir bütün olarak hareket bir kez daha bireysel dengeyi yok eder. (...) Tüm dengeler yalnızca göreceli ve geçicidir." [21]
Denge kategorisini daha iyi anlamak artık mümkün. Marksistler bu kategorinin meşruiyetini inkar etmezler. Ancak doğru anlaşılması gerekir. Hareket boşlukta gerçekleşmez. Karşıtların mücadelesinden kaynaklanır. Böyle bir mücadele ancak bu karşıtlar arasında bir ilişki varsa gerçekleşebilir. Bu tür ilişkilerin toplamı bir tür (geçici) denge oluşturur. Ancak bu ilişki sürekli hareket halindedir çünkü "gerçeklik bir 'yaratım ve yıkım sürecidir'" - Stalin tarafından ezilmeden önce 1920'lerde genç Sovyetler Birliği'ndeki felsefi tartışmalara hakim olan büyük diyalektik okulun önde gelen filozofu Abram Deborin'in belirttiği gibi. [22]
Dolayısıyla, materyalist diyalektik açısından bakıldığında, açık bir diyalektik hiyerarşi vardır. Deborin ekolünün bir diğer önde gelen filozofu ve Troçki'nin Sol Muhalefetinin destekçisi olan N.A. Karev, Bogdanov'un denge teorisine yönelik bir eleştirisinde şu açıklamayı yapmıştır
"Dolayısıyla Engels, şu ya da bu denge durumunun gerçekte var olmayacağını söylemiyor. Ancak bunlar geçicidir, maddelerin hareketinde yalnızca anları oluştururlar, yalnızca şu ya da bu an biçimiyle ilişki içinde anlam kazanırlar, sınırlı bir hareketin sonucudurlar. Dolayısıyla, denge durumları hareket ve gelişim sürecinde ikincil ve geçici anlardır. Temel ve belirleyici olan harekettir." [23]
Karev'in Bogdanov'a yönelttiği eleştiri, bize Promise Li ve POLOP tarafından savunulan "antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramına da çok uygun görünüyor.
"Bogdanov'un denge teorisi temelde dinamik değil statik bir bakış açısına dayanır, çünkü verili bir cismin hareket anını değil statik durum anını belirleyici olarak kabul eder. 'Hareketli' denge kategorisi sorunu çözmez çünkü hareketliliği dengenin ihlali olarak görür, tersini değil - denge durumu hareket süreci içinde geçici ve göreceli bir istikrar anıdır. Denge ve hareketin birliği burada denge kategorisi vurgulanarak anlaşılırken, diyalektik bir cismin her zaman ve her yerde ona içkin olan hareketini vurgular." [24]
Bu da bizi kısa felsefi gezintimizin son noktasına getiriyor. Harekete neden olan zıtların mücadelesinin merkeziliğini küçümsemek ve denge kavramını aşırı vurgulamak, gelişimin dinamiğini ve yönünü değerlendirememekle sonuçlanır. Denge durumuna saplanıp kalmış bir mekanist için her şey durağan ve pek hareket halinde değilmiş gibi görünür. Gerçekte, "yüzeyin altında" derin gelişmeler meydana gelir ve bunlar ancak karşıtların mücadelesinin neden olduğu hareketlerin geçici bir ifadesi olarak verili bir duruma ("denge") diyalektik olarak yaklaşıldığında fark edilebilir.
Günlük hayattan basit bir benzetme yapmak gerekirse. Eğer bir kişi evde su pişiriyorsa, çoğu zaman büyük değişiklikler gözlemlemez. Su değişmemiş gibi görünür... ta ki kaynamaya başladığı son anlara kadar. Bu, zamanın %99'unda hiçbir şey olmadığı ve suyun sadece bir denge durumunda olduğu anlamına mı gelir? Durumun böyle olmadığını, bu dönemde "gizli" bir ısınma sürecinin gerçekleştiğini bilmek için fizik doktoru olmanıza gerek yok.
Benzer şekilde, dünya siyasetindeki ve ekonomisindeki gelişmeleri analiz eden Marksistler de sadece yüzeyde görünen olguları gözlemlemekle yetinmemelidir. Yüzeyin altına bakmalı ve önümüzdeki kırılmalar ve patlamalarla birlikte gelişmenin yönünü anlamak için biriken çelişkilerin süreçlerini tanımlamalıdırlar. Deborin'in bir zamanlar söylediği gibi: "Bir Marksisther şeyden önce gelişmenin genel yönünü belirlemelidir." [25]
Ancak bu, ancak materyalist ve diyalektik bir yöntem uygulandığında ve mekanik denge teorisinin sadece uyuşuk bir durgunluğun yanılsamalı bir resmini çizen doktriner şemalarından kaçınıldığında mümkündür. Hegel,yöntemin "ruh ve öz" olduğunu ve "herhangi bir şeyin ancak yönteme tamamen boyun eğdirildiğinde hakikatiyle kavranıp bilinebileceğini" belirtmiştir [26] Ve gerçekten de materyalist diyalektik yöntem olmadan, modern emperyalizmin dinamiğini anlamak mümkün değildir.
Sonunda, Buharin'in mekanik yöntemi kapitalizmin çürümesinin ve buna eşlik eden savaşlar, devrimler ve karşı devrimler süreçlerinin tanınmasını engeller.
21. yüzyılda kapitalizm: büyüme dinamiğini geri kazanmak mı?
Yukarıda da belirtildiği üzere, Promise Li makalesinde emperyalist güçler arasında (ve ayrıca Küresel Güney'deki ulusal burjuvazilerle) işbirliği unsurlarının hakim olduğunu vurgulamaktadır. Aynı şekilde, kapitalizmin tekrarlanan krizlerle karşı karşıya olduğunu kabul etmekle birlikte, bunların üstesinden gelme ve büyümeyi yeniden sağlama kapasitesini de gösterdiğine inanmaktadır (her ne kadar bunun otomatik bir süreç olmadığını, siyasi müdahaleye ihtiyaç duyduğunu söylese de).
"Ancak bu karşılıklı bağımlılığı, sistemin dengeye doğru hareketsiz bir eğilimi olarak da algılamamalıyız. Gerçekte bu işbirliğinin sürdürülmesi, özellikle de kapitalist sistem kendi iç çelişkilerinden kaynaklanan krizlerin tekrar tekrar ortaya çıkmasını ele almak zorunda kaldıkça, sürekli bakım gerektirir. Örneğin 1970'lerdeki ve 2000'lerdeki karlılık krizleri, büyümeyi (ve işçi sınıfı isyanının bastırılmasını) yeniden sağlamak için kapitalizmin örgütlenme biçiminde köklü dönüşümler gerektirmiştir. Dolayısıyla, işbirliği koşullarının sürdürülebilmesi için bilinçli olarak yeniden keşfedilmesi gerekmektedir."
Buna karşılık, biz kapitalizmin 1970'lerin ortalarında uzun vadeli bir kriz dönemine - ya da bir "düşüş eğrisine" (Troçki'nin 1923'te düşünceli bir makalede detaylandırdığı "kapitalist gelişme eğrileri" kavramından bir kategori kullanacak olursak) girdiğini düşünüyoruz. [27] Bu kriz süreci 2008/09'daki Büyük Durgunluk ve o tarihten bu yana yaşanan yeni dönemle birlikte daha da derinleşmiştir. [28]
Doğal olarak bu çürüme doğrusal bir süreç değildir çünkü a) kapitalist yeniden üretim inişli çıkışlı iş çevrimlerinde ilerler ve b) karşıt eğilimler de mevcuttur. Bununla birlikte, uzun vadede düşüş eğilimi hakimdir ve bu çok sayıda olguyla tespit edilebilen bir süreçtir.
En önemlisi, insanlığın büyüyen kesimleri için yıkıcı sonuçları olan yıkıcı iklim değişikliğine yansıyan derin bir uygarlık krizi vardır. [29] Aynı şekilde, kapitalist dünya ekonomisinde durgunluk ve gerilemeye doğru açık bir eğilim vardır ve bu da artan göç dalgaları, sosyal sefalet ve daha fazla savaşla sonuçlanmaktadır. Aynı süreçle bağlantılı olarak, emperyalist güçler arasında hızlanan askerileşme ve rekabet de söz konusudur. Büyük Güçlerin doğrudan ya da dolaylı olarak dahil olduğu ve diğer ülkelere yayılma potansiyeli taşıyan iki büyük savaş -Ortadoğu ve Ukrayna'da- bunun güçlü örnekleridir.
Bu konuları çeşitli vesilelerle ele aldığımız için, kapitalist dünya ekonomisinin gerileyen dinamiğini gösteren birkaç rakam sunmakla yetineceğiz. Tablo 1 ve Şekil 1'deki rakamlardan da görebileceğimiz gibi, 1950'lerden bu yana Gayri Safi Yurtiçi Hasıla (GSYİH) büyüme oranlarında - hem toplamda hem de kişi başına - sürekli bir düşüş yaşanmıştır. Bu tabloların, 2019'un sonlarında başlayan ve 1929'dan bu yana en kötü çöküşü içeren dünya ekonomisindeki Büyük Buhran rakamlarını içermediğine dikkat edilmelidir.
Tablo 1: Küresel GSYH'nin Yıllık Ortalama Büyümesi 1960-2019 [30]
|
1970s |
1980s |
1990s |
2000s |
2011-1 |
2019 |
|
|
4.9% |
3.93% |
2.95% |
2.70% |
2.58% |
2.75% |
2.5% |
Kapitalist ekonomilerin büyüme oranlarındaki bu düşüş, kâr oranındaki düşüşle el ele gitmekte ya da daha ziyade bu düşüşe neden olmaktadır - ki bu da sonuçta toplam sermaye içinde canlı emeğin azalan ve ölü emeğin (makineler ve hammaddeler) artan payının bir sonucudur. Marx'ın bir keresinde belirttiği gibi, "bu yasa, ki ekonomi politiğin en önemli yasasıdır, kâr oranının kapitalist üretimin ilerlemesiyle birlikte düşme eğiliminde olmasıdır." [32]
Şekil 2'de son yetmiş yılda en büyük 20 ekonomide (G20 ülkeleri) kar oranının gelişimini gösteriyoruz. Gördüğümüz gibi, Marx'ın öngördüğü gibi, son yetmiş yılda kar oranında böyle uzun vadeli bir eğilim olmuştur.
Dolayısıyla, egemen sınıfın sayısız siyasi müdahalesine ve "antagonistik işbirliğine" rağmen dünya kapitalizminin eski büyüme oranlarına ulaşamadığını açıkça görebiliyoruz. Uzun süreli bir durgunluk ve gerileme dönemine sıkışıp kalmıştır.
Çin ve Rus emperyalizminin yükselişini abartıyor muyuz?
Yukarıdaki alıntıdan da anlaşılacağı üzere Li, benim ve benim gibi düşünen yazarların "ABD hegemonyasının gerilemesini aşırı derecede küçümseyip, ABD emperyalizmine karşı bir denge unsuru olarak yeni emperyalistlerin yükselişini abarttığımıza" inanıyor. Ne yazık ki bu iddiasını kanıtlayacak tek bir alıntı bile yapmıyor. Dolayısıyla Li'nin neden ABD hegemonyasının gerilemesini hafife aldığımı düşündüğü konusunda en ufak bir fikrim yok. Her halükarda, eleştirisinin haklı olmadığını düşünüyorum.
Çin'in kapitalist sınıfının yerli işçi sınıfı pahasına kendisini büyük ölçüde zenginleştirmekle kalmayıp, aynı zamanda dünya pazarında ABD'ye meydan okuyabildiğini bir dizi çalışmada gösterdik. Yine, bu gelişmeyi birkaç rakamla göstermekle yetiniyor ve ilgilenen okuyucuları daha ayrıntılı çalışmalara yönlendiriyorum. [34]
Aşağıdaki tablolarda Çin'in uzun zamandır hegemon olan ABD emperyalizmini hızla yakaladığını gösteriyoruz. Tablo 2'de Çin'in küresel imalat üretimindeki payının 2000 yılında ABD'nin yarısından az olduğunu görüyoruz (%9,8'e karşı %23,7); ancak 2022 yılına gelindiğinde Çin'in payı Batılı rakibinin neredeyse iki katına ulaşmıştır (%30,7'ye karşı %16,1).
Tablo 2. Küresel Üretimde İlk Altı Ülke Küresel Üretimde İlk Altı Ülke, 2000 ve 2022 [35]
|
Rank |
Countr |
Share 2000 |
Share 2022 |
|
1. |
China |
9.8% |
30.7% |
|
2. |
U.S. |
23.7% |
16.1% |
|
3. |
Japan |
10.2% |
6.0% |
|
4. |
Germany |
6.4% |
4.8% |
|
5. |
South Korea |
2.5% |
3.1% |
|
6. |
India |
1.4% |
3.1% |
Dünyanın önde gelen şirketlerinin ulusal kompozisyonuna ve milyarderlerin küresel sıralamasına baktığımızda da benzer bir tablo görüyoruz (Tablo 3-5). Tüm bu kategorilerde Çin, ABD'nin önünde ya da arkasında 1 ya da 2 numara haline gelmiştir.
Tablo 3. Fortune Global 500 Fortune Global 500 Şirketleri Sıralamasında İlk 10 Ülke (2023) [36]
|
Rank |
Country |
Companies |
Share (in%) |
|
|
1 |
United States |
136 |
27.2% |
|
|
2 |
China (excl. Taiwan) |
135 |
27.0% |
|
|
3 |
Japan |
41 |
8.2% |
|
|
4 |
Germany |
30 |
6.0% |
|
|
5 |
France |
23 |
4.6% |
|
|
6 |
South Korea |
18 |
3.6% |
|
|
7 |
United Kingdom |
15 |
3.0% |
|
|
8 |
Canada |
14 |
2.8% |
|
|
9 |
Switzerland |
11 |
2.2% |
|
|
10 |
Netherlands |
10 |
2.0% |
|
Tablo 4. Forbes Milyarderler 2023 Listesinin İlk 5 Ülkesi [37]
|
Rank |
Country |
Number of billionaires |
|
1 |
United States |
735 |
|
2 |
China (incl. Hong Kong) |
561 |
|
3 |
India |
169 |
|
4 |
Germany |
126 |
|
5 |
Russia |
105 |
Tablo 5. Hurun Küresel Zenginler Listesi Hurun Küresel Zenginler Listesi 2024'ün İlk 10 Ülkesi [38]
|
Rank |
Country |
Number of billionaires |
|
1 |
China (incl. Hong Kong) |
814 |
|
2 |
U.S. |
800 |
|
3 |
India |
271 |
|
4 |
United Kingdom |
146 |
|
5 |
Germany |
140 |
|
6. |
Switzerland |
106 |
|
7. |
Russia |
76 |
|
8. |
Italy |
69 |
|
9. |
France |
68 |
|
10. |
Brazil |
64 |
Rusya aynı zamanda iç pazara hakim olan ve başta Orta Asya ve Doğu Avrupa olmak üzere çeşitli ülkelere sermaye ihraç eden tekelci bir sermaye geliştirmiştir. Yaklaşık üç yıldan beri Ukrayna Savaşı nedeniyle tüm Batılı güçler tarafından uygulanan benzeri görülmemiş yaptırım dalgasına direnmeyi başarması da Rusya'nın ekonomik gücünü ortaya koymuştur. Ancak, son zamanlarda PPP (Satın Alma Gücü Paritesi) açısından Almanya ve Japonya'nın GSYH'sini geçmesine rağmen dünya pazarındaki konumu oldukça zayıftır. [39]
Rusya ekonomik olarak ABD ve Çin'in açık bir şekilde gerisinde olsa da askeri alanda lider bir güçtür. En büyük nükleer cephaneliğe ve üçüncü en yüksek askeri harcamaya sahiptir. (Bkz. Tablo 6 ve 7) Ayrıca, nüfuzunu genişletmek, halk isyanlarını bastırmak ya da müttefiki olan bir diktatörlüğü iktidarda tutmak amacıyla diğer ülkelerde gerçekleştirdiği çok sayıda askeri müdahaleyle askeri saldırganlığını göstermiştir (örneğin Çeçenistan, Gürcistan, Kazakistan, Suriye, Libya, Mali, vb.) [40].
Tablo 6. Dünya Nükleer Güçleri, 2024 [41]
|
Country |
Total Military Stockpile |
Total Inventory (incl. Retired Warheads) |
|
Russia |
4,380 |
5,580 |
|
United States |
3,708 |
5,044 |
|
China |
500 |
500 |
|
France |
280 |
290 |
|
United Kingdom |
225 |
225 |
|
India |
172 |
172 |
|
Pakistan |
170 |
170 |
|
Israel |
90 |
90 |
|
North Korea |
50 |
50 |
Tablo 7. Askeri Harcamalar, Milyar ABD Doları Olarak Dünya Harcamaları İçindeki Payı, 2023 [42]
|
|
|
Spending ($billion) |
Share of World Spending |
|
1. |
United States |
916 |
37% |
|
2. |
China |
296 |
12% |
|
3. |
Russia |
109 |
4.5% |
Dahası, BRICS'in genişlemesinin de gösterdiği gibi Çin ve Rusya yakın zamanda etki alanlarını önemli ölçüde genişletti. Dört devlet - Mısır, Etiyopya, İran ve Birleşik Arap Emirlikleri - 2024 yılının başında beş orijinal BRICS üyesine (Brezilya, Rusya, Hindistan, Çin ve Güney Afrika) resmen katıldı. Bir ülke, Suudi Arabistan, katılmaya davet edildi ancak henüz bu konuda karar vermiş değil. Ve Ekim 2024'te 13 ülke daha "ortak ülke" olarak adlandırıldı (Cezayir, Belarus, Bolivya, Küba, Endonezya, Kazakistan, Malezya, Nijerya, Tayland, Türkiye, Uganda, Özbekistan ve Vietnam).
Yukarıda Claudi Katz'a verdiğim yanıtta daha ayrıntılı olarak açıkladığım üzere, BRICS+ 2023'te dokuz üye ülkeye genişledikten sonra yaklaşık 3,5 milyarlık bir toplam nüfusa ya da dünya nüfusunun %45'ine (yeni "ortak ülkeler" de dahil edilirse bu oran yarıdan fazla olacaktır) sahip olacaktır. Birleşik GSYİH'si - hesaplama yöntemine bağlı olarak - ya Batılı Büyük Güçlerin (G7) 1/3'ünden biraz daha geride ya da eski emperyalist güçleri çoktan aşmış durumda. Aynı şekilde BRICS+, kapitalist değer üretiminin ana sektörü olan toplam dünya sanayi üretiminin %38,3'ünü gerçekleştirmektedir.
Enerji kaynaklarına gelince, BRICS+ üyeleri dünya petrol rezervlerinin %47'sine ve doğal gaz rezervlerinin %50'sine sahiptir. [43] 2024 yılı itibariyle BRICS, yeni üyeleriyle birlikte dünyadaki nadir toprak metal rezervlerinin yaklaşık %72'sini kontrol etmektedir. [44]
BRICS+'nın homojen ve merkezi bir ittifak olmadığı elbette doğrudur. Yine de Modi ve Putin'in vurguladığı gibi, Çin ve Rus emperyalizminin hakim olduğu "batılı olmayan bir grup". Ayrıca BRICS+ ülkeleri kapitalist açıdan daha az gelişmiş ve daha düşük yaşam standartlarına sahiptir.
Bununla birlikte Li, Çin ve Rusya'nın yeni emperyalist güçler olarak yükselişini abarttığımı düşünürken, ben onun bu süreci hafife aldığını ve sonuç olarak emperyalistler arası rekabetin hızlanmasını da hafife aldığını düşünüyorum. NATO ve Rusya arasındaki askeri tehditler ve nükleer kılıç şakırtıları ile Washington ve Pekin arasında Güney Çin Denizi'nde ve Tayvan çevresinde hızlanan askeri gerilimler, emperyalist sistemin "antagonistik işbirliği "nden ziyade antagonistik çelişkilerle karakterize olduğunun açık göstergeleridir.
Bu nedenle, SIPRI'nin rapor ettiği gibi, küresel askeri harcamaların 1990'ların ortalarından bu yana yıldan yıla artması ve şu anda - toplam 2,443 milyar dolarla - 30 yıl öncesine göre yaklaşık iki kat daha yüksek olması şaşırtıcı değildir. [45]
Hızlanan emperyalistler arası rekabet sadece silahlanma ve askeri gerilimlerle sınırlı değil. ABD, Çin, AB ve Rusya arasında artan korumacılıkla birlikte tırmanan bir ticaret savaşı da söz konusudur. Aslında küreselleşme, onlarca yıllık muazzam büyümenin ardından 2008'deki Büyük Durgunluk'tan bu yana sona ermiştir ("Küreselleşme"). O zamandan bu yana, yani 15 yılı aşkın bir süredir, dünya mal ticaretinin küresel üretimdeki payı %51,2'den (2008) %45,8'e (2023) gerilemiştir. [46]
Dolayısıyla Li, "neoliberal dünya düzenini yıkmak bir yana, kapitalist sınıf küreselleşmeyi sürdürmek ve reforme etmek için yeni terimler icatediyor" derken, emperyalist güçler arasındaki ilişkilerin gelişim yönünü tamamen yanlış anlıyor.
Tüm bu nedenlerden dolayı, Li'nin Batılı ve Doğulu güçler arasında "yeni bir Soğuk Savaş" kategorisine neden itiraz ettiğini ve bunu "ideolojik bir kurgu" olarak nitelendirdiğini anlamak zordur. Emperyalist güçler arasında bir başka dünya savaşına işaret eden yükselen militarizmi ve rekabetin hızlanmasını görmüyor mu?
Daha önce de ısrarla vurguladığım gibi, Marksistler yaklaşan kırılma ve patlamaları anlamak için "gelişmenin genel yönünü belirlemelidir". Li'nin "antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramı, mevcut dünya durumunun dinamiklerini anlamaya yardımcı olmuyor.
Kapitalist karşılıklı bağımlılık emperyalistler arası savaş için bir engel midir?
Son olarak Li'nin makalesinde ortaya koyduğu bir başka önemli argümana değinelim. Yukarıdaki alıntılarda gösterildiği gibi, "ekonomik karşılıklı bağımlılığın" modern emperyalizmin temel bir özelliği olduğunu ve sonuç olarak bunun güçler arasındaki "antagonistik işbirliğinin" maddi temelini oluşturacağını savunuyor. Hatta böyle bir ekonomik karşılıklı bağımlılığın emperyalistler arası bir savaşı imkânsız ya da en azından ihtimal dışı kılacağını düşünmektedir.
"Gerçekten de, Birinci Dünya Savaşı sırasında küresel ekonomik entegrasyon göze çarpan biçimlerde varlığını sürdürüyordu, ancak çoğunlukla tarihçi Jamie Martin'in "gergin karşılıklı bağımlılık" olarak adlandırdığı jeopolitik kamplar içinde yer alıyordu. Ancak neoliberalizmin yükselişi, rakip devlet blokları arasında bile devam eden bir karşılıklı bağımlılık düzeyi geliştirdi ve böylece ilk iki Dünya Savaşı'nda tanık olunan açık emperyalist savaş olasılığının altını oydu."
Bunun hem metodolojik hem de tarihsel olarak yanlış olduğunu düşünüyoruz. Buharin'in yukarıda belirtilen alıntılarda doğru bir şekilde işaret ettiği gibi, karşılıklı bağımlılık sadece ekonomik bağları derinleştirmekle kalmaz, aynı zamanda rekabeti de hızlandırır. Geçtiğimiz yıllarda Çin ve ABD birbirlerinin en önemli ticaret ortakları arasında yer almıştır. Ancak bu durum, bu güçlerin bir ticaret savaşı başlatmasını ve hızlandırmasını engellemedi. Aynı durum şu anda Çin ile Avrupa Birliği arasında yaşanmakta olup, Avrupa Birliği Çin'den ithal edilen mallara önemli gümrük vergileri uygulamaktadır. Doğru, her iki taraftaki büyük şirketler de bu gelişmeden memnun değil. Ancak sonuçta kapitalizmin nesnel yasalarına ve emperyalistler arası rekabetin doğasına boyun eğmek zorundalar.
Yukarıda bahsettiğim Büyük Güç rekabeti hakkındaki kitabımda da tartıştığım gibi, böyle bir gelişmenin tarihi bir emsali de mevcuttur. Birinci Dünya Savaşı'ndaki iki büyük rakip olan İngiltere ve Almanya, 1914'ten önce yakın ekonomik ilişkilere sahipti. [47] Tablo 8'de 1914 öncesinde İngiltere'nin Almanya'nın en önemli ticaret ortağı olduğunu (ABD ise ikinci sıradaydı), Almanya'nın ise İngiltere'nin ticareti için neredeyse Fransa kadar önemli olduğunu görüyoruz. Ancak bu ekonomik karşılıklı bağımlılık, bu güçlerin birbirlerine karşı en yıkıcı savaşı başlatmalarını engellememiştir.
Tablo 8. İngiltere ve Almanya'nın İngiltere ve Almanya'nın Başlıca Ticaret Ortakları, 1890-1913 (Ortalama % Pay) [48]
|
Britain |
Germany |
||
|
1. U.S.: |
19.47% |
1. Britain: |
13.85% |
|
2. France: |
8.99% |
2. U.S.: |
11.03% |
|
3. Germany: |
8.90% |
3. Austria-Hungary: |
10.15% |
Dolayısıyla, uzun vadede, emperyalist güçler arasında artan ekonomik karşılıklı bağımlılık daha istikrarlı bir kapitalist dünya sistemi ile sonuçlanmaz. "Antagonistik işbirliği" ile karakterize edilen bir emperyalizm türü yaratmaz; emperyalizm daha ziyade antagonistik çelişkilerle dolu bir sistem olarak kalır.
Sonuçlar
1. "Karşıtişbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramı, mevcut dönemde dünya durumunun dinamiklerini anlamaya izin vermemektedir. Promise Li, sadece eski Batılı güçlerin değil, yeni Doğulu güçlerin (Çin ve Rusya) de emperyalist doğasını doğru bir şekilde kabul ederken, ortodoks emperyalizm teorisinin destekçilerini bunlar arasındaki rekabeti abartmakla yanlış bir şekilde eleştirmektedir.
2. Promise Li ve Brezilyalı Política Operária kolektifinin, emperyalizm kavramının öncüleri olarak August Thalheimer ve Nikolai Bukharin'e "antagonistik işbirliği" şeklinde atıfta bulunması yanıltıcıdır. Buharin, şematizm konusundaki zayıflıklarına rağmen, emperyalist güçler arasında kaçınılmaz olarak savaşlarla sonuçlanmak zorunda olan rekabet ve antagonizmayı vurgulamıştır. Thalheimer'in 1946'da emperyalist güçler arasında "antagonistik işbirliği" tezini geliştirdiği doğrudur. Ancak bu, a) Stalinist devletlerin muazzam genişlemesi ve b) İkinci Dünya Savaşı'nın ABD'nin emperyalist devletler arasında mutlak hegemon olmasıyla sonuçlanmasıyla karakterize edilen belirli bir küresel durumun (doğru) bir tanımıydı. Dolayısıyla, emperyalist güçler arasında daha fazla işbirliği tezi, yeni bir dünya savaşına işaret eden Stalinist devletlere karşı kolektif saldırgan yaklaşımlarıyla doğrudan ilişkiliydi. Bu nedenle Thalheimer, emperyalistler arası gerilimin azalacağını, çünkü emperyalist devletler ile yozlaşmış işçi devletleri arasındaki gerilimin muazzam bir ivme kazanmasıyla bastırılacağını düşünüyordu. Ancak Stalinizm 1989-91'de çöktüğünden, Thalheimer'ın kavramı bugün artık emperyalizm için geçerli değildir.
3. Thalheimer'ın siyasi akıl hocası Buharin'in, diyalektik materyalizmin sadık bir muhalifi olan Alexander Bogdanov'un felsefesinden etkilendiği doğrudur. Dolayısıyla, hareketin itici gücü olarak iç çelişkilerin rolünü küçümseyen bir kavram olan mekanist denge teorisini içeren bir dünya görüşünü savunmuştur. Sonuç olarak, bu yöntemin destekçileri dengeyi maddenin temel özelliği olarak görürken, aslında denge daha ziyade harekettir. Dolayısıyla, Buharinci yöntem dünya durumundaki kırılma, kriz ve patlama eğilimlerini hafife almakta, istikrar ve dengeyi ise abartmaktadır. "Antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramı bu tür metodolojik eksikliklerden muzdariptir.
4. Materyalist diyalektik açısından, karşıtların birliği ve mücadelesinin neden olduğu iç çelişkiler hareketin itici gücüdür. Mekanist yöntem şu soruyu doğru yanıtlamaktan acizdir: Maddenin belirleyici özelliği nedir - denge ya da çelişki durumu, karşıtların mücadelesinin bir sonucu olarak hareket? Materyalist diyalektik açısından doğru yanıt, karşıtların mücadelesinin, çelişkinin, harekete, dönüşüme, ilerlemeye neden olduğu için belirleyici özellik olduğudur. Buna karşılık, denge durumu yalnızca geçici bir andır.
5. Buharin'in mekanist denge teorisi ile "antagonistik işbirliği" olarak emperyalizm kavramı arasında açık bir bağlantı vardır. Karşıtların mücadelesini ve harekete neden olan iç çelişkileri küçümseyen felsefe, gerçekliğin (hareketli) bir denge durumu olarak anlaşılmasıyla sonuçlanır. Böyle bir metodolojik temelde, dünyadaki durumu öncelikle göreceli istikrar ve emperyalistler arasındaki işbirliği ile karakterize edilen bir durum olarak görmek kolaylaşır. Sonuç olarak, kafalar karışır ve dünya siyasetinin ve ekonomisinin hareket yönü fark edilemez.
6. Sonuç olarak, Promise Li, emperyalist dünya sisteminin hem ekonomik hem de siyasi olarak krizlerle dolu karakterini ve çürümesini yeterince dikkate almamaktadır. Kapitalist dünya ekonomisi uzun vadeli durgunluk ve gerilemeye hapsolmuş durumda, iklim değişikliği insanlığın hayatta kalmasını tehdit ediyor, sosyal sefalet ve savaşlar yayılıyor.
7. Promise Li'nin Çin ve Rus emperyalizminin yükselişini abarttığımız yönündeki eleştirisi, son bir, yirmi yılda Büyük Güçler arasındaki güçler ilişkisinde meydana gelen niteliksel değişiklikleri göz ardı etmektedir. Doğulu emperyalistler uzun süredir devam eden Batı hegemonyasına ekonomik, siyasi ve askeri olarak ciddi bir şekilde meydan okumaktadır. Aslında Li'nin eleştirisi, emperyalistler arası rekabeti hafife alması ve "antagonistik işbirliğinin" dünya durumunun temel özelliği olacağı görüşüyle ilgilidir.
8. Promise Li, "ekonomik karşılıklı bağımlılığın" modern kapitalizmin temel bir özelliği olduğunu ve bunun "emperyalistler arası açık savaş olasılığını ortadankaldıracağını" iddia etmektedir. Ancak tarih bunun doğru olmadığını göstermiştir. Uzun vadede, emperyalist güçler arasında artan ekonomik karşılıklı bağımlılık daha istikrarlı bir kapitalist dünya sistemi ile sonuçlanmaz. "Antagonistik işbirliği" ile karakterize edilen bir emperyalizm türü yaratmaz; emperyalizm daha ziyade antagonistik çelişkilerle dolu bir sistem olarak kalır.
[1] Michael Pröbsting: "İmparatorluk" çağında mı yoksa emperyalizm çağında mı yaşıyoruz? Marksist emperyalizm teorisinin güncelliği üzerine Claudio Katz'a bir başka yanıt, 16 Kasım 2024, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/are-we-living-in-the-age-of-empire-or-of-imperialism-3rd-reply-to-claudio-katz/
[2] Promise Li: Antagonistik İşbirliği Olarak Emperyalizm, 15 Ekim 2024, https://spectrejournal.com/imperialism-as-antagonistic-cooperation/; https://links.org.au/imperialism-antagonistic-cooperation. Aksi belirtilmediği sürece tüm alıntılar bu makaleden yapılmıştır.
[3] Marksist emperyalizm teorisi üzerine en detaylı çalışmalarım iki kitaptır: Büyük Güç Rekabeti Çağında Anti-Emperyalizm. ABD, Çin, Rusya, AB ve Japonya Arasında Hızlanan Rekabetin Arkasındaki Faktörler. A Critique of the Left's Analysis and an Outline of the Marxist Perspective, RCIT Books, Viyana 2019, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/anti-imperialism-in-the-age-of-great-power-rivalry/; The Great Robbery of the South. Continuity and Changes in the Super-Exploitation of the Semi-Colonial World by Monopoly Capital Consequences for the Marxist Theory of Imperialism, RCIT Books, 2013, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/great-robbery-of-the-south/
[4] Promise Li: 21. yüzyılda ABD-Çin rekabeti, 'antagonistik işbirliği' ve anti-emperyalizm, 14 Eylül, 2023, https://links.org.au/us-china-rivalry-antagonistic-cooperation-and-anti-imperialism-21st-century
[5] "Alt-emperyalizm" teorisinin bir eleştirisi için bkz. örneğin benim makalem: Yarı Sömürge Ara Güçler ve Alt-Emperyalizm Teorisi. Marksistler arasında süregelen bir tartışmaya katkı ve teorik bir sorunun üstesinden gelmek için bir öneri, 1 Ağustos 2019, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/semi-colonial-intermediate-powers-and-the-theory-of-sub-imperialism/; ayrıca bkz. yukarıda bahsi geçen "Büyük Güç Rekabeti Çağında Anti-Emperyalizm" kitabımızın IV. bölümü ("Emperyalist Büyük Güç için Marksist Kriterler")
[6] Buharin'in faydalı biyografileri örneğin Stephen Cohen: Buharin ve Bolşevik Devrimi. A Political Biography, 1888-1938. Oxford University Press, 1980; Wladislaw Hedeler: Nikolai Bucharin. Stalins tragischer Opponent. Eine politische Biographie. Matthes & Seitz, Berlin 2015; Adolf G. Löwy: Die Weltgeschichte ist das Weltgericht. Leben und Werk Nikolai Bucharins. Promedia-Verlags-Gesellschaft, Wien 1990; Anna Larina: This I cannot forget. Nikolai Bukharin'in Dul Eşinin Anıları. W. W. Norton & Co, New York 1993.
[7] Sağ Muhalefet'in İngilizce tarihi hakkında bkz. örneğin Robert J. Alexander: Sağ Muhalefet. The Lovestoneites and the International Communist Opposition of the 1930s, Greenwood Press, Londra 1981
[8] August Thalheimer: Grundlinien und Grundbegriffe der Weltpolitik nach dem 2. Weltrieg, Gruppe Arbeiterpolitik, 1946, s. 11 ve 9 (çevirimiz). Weltkrieg, Gruppe Arbeiterpolitik, 1946, s. 11 ve 9 (bizim çevirimiz)
[9] Nikolai Bukharin: Imperialism and World Economy (1915), International Publishers, New York 1929, s. 104
[10] Nikolai Bukharin: The Politics and Economics of the Transition Period (1920), Routledge, Abingdon 2003, s. 63-64
[11] Nikolai Bukharin: Emperyalizm ve Dünya Ekonomisi, s. 148
[12] A.g.e., s. 54
[13] Alexander Bogdanov hakkında bkz. örneğin James D. White: Kızıl Hamlet: The Life and Ideas of Alexander Bogdanov, Brill, Leiden 2018; Dietrich Grille: Lenins Rivale: Bogdanov und seine Philosophie, Verlag Wissenschaft und Politik, Köln 1966; ayrıca Vadim N. Sadovsky ve Vladimir V. Kelle tarafından yazılan Bogdanov's Tektology Cilt 1'in önsözüne bakınız, Centre for Systems Studies, University of Hull, 1996, s. iii-xxii; V.A. Bazarov: Bir Düşünür Olarak Bogdanov, içinde: Alexander Bogdanov: Empiriomonism. Essays in Philosophy, Books 1-3, Brill, Leiden 2020, s. xvii-xli.
[14] Nikolai Bukharin: Tarihsel Materyalizm. A System of Sociology (1921), Üçüncü Rusça baskıdan Yetkili Çeviri, George Allen & Unwin, Ltd, Londra 1926, s. 74
[15] V.I. Lenin: Diyalektik Sorunu Üzerine (1915); içinde: CW 38, s.358
[16] Nikolai Bukharin: Tarihsel Materyalizm, s. 79
[17] A.g.e., s. 74
[18] Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel: Science of Logic, George Allen & Unwin, Ltd, New York 1969, s. 439 (ayrıca V.I. Lenin'den alıntılanmıştır: Hegel'in Mantık Bilimi (1914) Kitabının Konspektüsü; içinde: LCW 38, s. 178-179)
[19] Friedrich Engels: Anti-Dühring. Herr Eugen Dühring'in Bilimdeki Devrimi, in: MECW Cilt 25, s. 55-56
[20] V.I. Lenin: Diyalektik Sorunu Üzerine (1915); içinde: LCW 38, s.358
[21] Friedrich Engels: Doğanın Diyalektiği, içinde: MECW Cilt 25, s. 525-526
[22] Abram Deborin: Lenin als revolutionärer Dialektiker (1925); in: Nikolai Bucharin, Abram Deborin: Kontroversen über dialektischen und mechanistischen Materialismus, Frankfurt a.M. 1974, s. 54 (bizim çevirimiz)
[23] N.A. Karew: Die Theorie des Gleichgewichts und der Marxismus; in: Wilhelm Goerdt (Hrsg.): Die Sowjetphilosophie. Wendigkeit und Bestimmtheit. Dokumente, Darmstadt 1967, s. 139 (bizim çevirimiz)
[24] A.g.e., s. 140-141
[25] Abram Deborin: Lenin als revolutionärer Dialektiker (1925); in: Unter dem Banner des Marxismus, 1. Jahrgang (1925-26), s. 224 (bizim çevirimiz)
[26] Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel: The Science of Logic, (Translated by A.V. Miller), Humanity Books, New York 1969, s. 826
[27] Leon Troçki: The capitalist curve of development (1923), içinde: Leon Troçki: Problems of Everyday Life, New York, 1994, s. 273-280
[28] Mevcut tarihsel döneme ilişkin analizlerimiz için yukarıda bahsi geçen "Güney'in Büyük Soygunu" kitabının 14. bölümüne ve yine yukarıda bahsi geçen "Büyük Güç Rekabeti Çağında Anti-Emperyalizm" kitabının I. ve II. bölümlerine bakınız.
[29] Bkz. örneğin RCIT: Tarım ve Ekoloji Üzerine Tezler, Eylül 2023, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/theses-on-agriculture-and-ecology/, Almedina Gunić: Emperyalizmin Ölümcül Nefesi, 23.10.2017, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/pollution-caused-the-death-of-9-million-people-in-2015/
[30] Murray E.G. Smith, Josh Watterton: Değerlenme, Finansallaşma ve Kriz: Zamansal Değer Teorik Bir Yaklaşım, 2021, s. 5
[31] M. Ayhan Köse, Franziska Ohnsorge (der.): A Decade since the Global Recession, Lessons and Challenges for Emerging and Developing Economies, Dünya Bankası, 2019, s. 9
[32] Karl Marx: 1861-63 Ekonomik El Yazmaları. Sermaye ve Kâr. 7) Kapitalist Üretimin İlerlemesiyle Birlikte Kâr Oranının Düşmesinin Genel Yasası; in: MECW, Cilt 33, s. 104-145; http://www.marxists.org/archive/marx/works/1861/economic/ch57.htm
[33] Michael Roberts: Küreselleşme sona mı erdi? (2022), https://thenextrecession.wordpress.com/2022/04/27/has-globalisation-ended/
[34] Çin'de kapitalizm ve onun emperyalist bir güce dönüşmesi hakkında çok sayıda eser yayınladım. Bunlardan en önemlileri şunlardır: Çin Emperyalizmi ve Dünya Ekonomisi, "The Palgrave Encyclopedia of Imperialism and Anti-Imperialism "in (Immanuel Ness ve Zak Cope editörlüğünde) ikinci baskısında yayınlanan bir deneme, Palgrave Macmillan, Cham, 2020, https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007%2F978-3-319-91206-6_179-1; Çin: "Komünist" Parti ve Kapitalistler Arasındaki İlişki Üzerine. Çin'in yönetici bürokrasisinin özgül sınıf karakteri ve son on yıllardaki dönüşümü üzerine notlar, 8 Eylül 2024, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/china-on-the-relationship-between-communist-party-and-capitalists/; Çin: Stalinizm, Kapitalist Restorasyon ve Marksist Devlet Teorisi Üzerine. Tek ve aynı parti rejimi altında toplumsal mülkiyet ilişkilerinin dönüşümü üzerine notlar, 15 Eylül 2024, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/china-on-stalinism-capitalist-restoration-and-marxist-state-theory/; Çin: Emperyalist Bir Güç... Yoksa Henüz Değil mi? Çok Pratik Sonuçları Olan Teorik Bir Soru! Esteban Mercatante ve PTS/FT ile Çin'in sınıf karakteri ve bunun devrimci strateji açısından sonuçları üzerine tartışmaya devam, 22 Ocak 2022, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/china-imperialist-power-or-not-yet/; Çin'in emperyalist bir güce dönüşümü. Büyük bir güç olarak Çin'in ekonomik, siyasi ve askeri yönleri üzerine bir çalışma (2012), in: Devrimci Komünizm No. 4, https://www.thecommunists.net/publications/revcom-1-10/#anker_4; Bazı Marksistlerin Çin'in Kapitalist Olduğundan Hala Şüphe Etmesi Nasıl Mümkün Olabilir? Çin'in Kamu İktisadi Teşebbüslerinin kapitalist karakteri ve bunun siyasi sonuçları üzerine bir analiz, 18 Eylül 2020, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/pts-ft-and-chinese-imperialism-2/; Unable to See the Wood for the Trees. Eklektik ampirizm ve PTS/FT'nin Çin'in emperyalist karakterini tanımadaki başarısızlığı, 13 Ağustos 2020, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/pts-ft-and-chinese-imperialism/; Çin'in Emperyalist Bir Güç Olarak Ortaya Çıkışı (ABD'deki 'New Politics' dergisindeki makale), in: "New Politics", Summer 2014 (Vol:XV-1, Whole #: 57). RCIT'in web sitesindeki özel bir alt sayfada daha birçok RCIT belgesine bakınız: https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/china-russia-as-imperialist-powers/.
[35] 2000 yılına ait rakamlar: APEC: Bölgesel Eğilimler Analizi, Mayıs 2021, s. 2; ilk sütundaki Almanya ve Hindistan rakamları 2005 yılına aittir (UNIDO: Industrial Development Report 2011, s. 194); 2022 yılına ait rakamlar: UNIDO: International Yearbook of Industrial Statistics Edition 2023, s. 36-37
[36] Fortune Global 500, Ağustos 2023, https://fortune.com/ranking/global500/2023/ (pay rakamları bizim hesaplamamızdır)
[37] Forbes: Forbes Milyarderler 2023, https://www.forbes.com/sites/chasewithorn/2023/04/04/forbes-37th-annual-worlds-billionaires-list-facts-and-figures-2023/?sh=23927e7477d7
[38] Hurun Küresel Zenginler Listesi 2024, 26.03.2024, https://www.hurun.net/en-US/Info/Detail?num=K851WM942LBU
[39] Bkz. örneğin Michael Pröbsting: Rusya Japonya'yı Geçerek Dünyanın En Büyük Dördüncü Ekonomisi Olacak, 5 Temmuz 2024, https://www.thecommunists.net/worldwide/global/russia-overtakes-japan-to-become-fourth-largest-economy-in-the-world/
[40] Rusya'da kapitalizm ve onun emperyalist bir güce dönüşmesi hakkında çok sayıda eser yayınladım. Bunların en önemlileri aşağıdaki broşürlerdir: Rus Emperyalizminin Kendine Özgü Özellikleri. A Study of Russia's Monopolies, Capital Export and Super-Exploitation in the Light of Marxist Theory, 10 Ağustos 2021, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/the-peculiar-features-of-russian-imperialism/; Lenin's Theory of Imperialism and the Rise of Russia as a Great Power. Lenin'in Emperyalizm Teorisi Işığında Günümüz Emperyalistler Arası Rekabetin Anlaşılması ve Yanlış Anlaşılması Üzerine. Rusya'nın Emperyalist Karakterini İnkar Eden Eleştirmenlerimize Bir Yanıt Daha, Ağustos 2014, http://www.thecommunists.net/theory/imperialism-theory-and-russia/; Büyük Bir Emperyalist Güç Olarak Rusya. Rus Tekelci Sermayesinin ve İmparatorluğunun Oluşumu, 18 Mart 2014, http://www.thecommunists.net/theory/imperialist-russia/.
[41] SIPRI Yıllığı 2024: Silahlanma, Silahsızlanma ve Uluslararası Güvenlik, s. 272
[42] Nan Tian, Diego Lopes Da Silva, Xiao Liang ve Lorenzo Scarazzato: Dünya Askeri Harcamalarındaki Eğilimler, SIPRI, 2023, s. 2
[43] Bu konuda bkz: Henry Meyer, S'thembile Cele ve Simone Iglesias: Putin BRICS Liderlerini Ağırlayarak İzole Edilmekten Uzak Olduğunu Gösterdi, Bloomberg, 22 Ekim 2024, https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2024-10-22/putin-hosts-brics-leaders-in-russia-defying-attempts-from-west-to-isolate-him; Dr. Kalim Siddiqui: BRICS Genişlemesi ve Batı'nın Ekonomik ve Jeopolitik Hakimiyetinin Sonu, 30 Ekim 2024, https://worldfinancialreview.com/the-brics-expansion-and-the-end-of-western-economic-and-geopolitical-dominance/; Walid Abuhelal: Can the Brics end US hegemony in the Middle East? Middle East Eye, 22 Ekim 2024 https://www.middleeasteye.net/opinion/can-brics-end-us-hegemony-middle-east; Anthoni van Nieuwkerk: BRICS+ ortak değerler ya da kimlik olmaksızın yeni bir dünya düzeni istiyor, 30 Ekim 2024 https://asiatimes.com/2024/10/brics-wants-new-world-order-sans-shared-values-or-identity/
[44] Ben Aris: BRICS G7'yi yenebilir mi? Intellinews, 19 Ekim 2024, https://www.intellinews.com/can-the-brics-beat-the-g7-348632/?source=south-africa
[45] Nan Tian ve diğerleri: Dünya Askeri Harcamalarındaki Eğilimler, s. 2
[46] Dünya Bankası: Mal ticareti (GSYH'nin %'si), 21 Kasım 2024 tarihinde erişilmiştir, https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/TG.VAL.TOTL.GD.ZS?view=chart
[47] Bu konuda bkz. örneğin Helga Nussbaum: Der europäische Wirtschaftsraum. Verflechtung, Angleichung, Diskrepanz, in: Fritz Klein, Karl Otmar von Aretin (Eds): Europea um 1900, Akademie-Verlag, Berlin 1989, s. 49
[48] Stefano Battilossi: The Determinants of Multinational Banking during the First Globalization, 1870-1914, Working Papers 114, Oesterreichische Nationalbank (Austrian Central Bank), 2006, s. 40
Şekil 1: Kişi Başına Küresel GSYH'nin Yıllık Ortalama Büyümesi 1950-2019 [31]
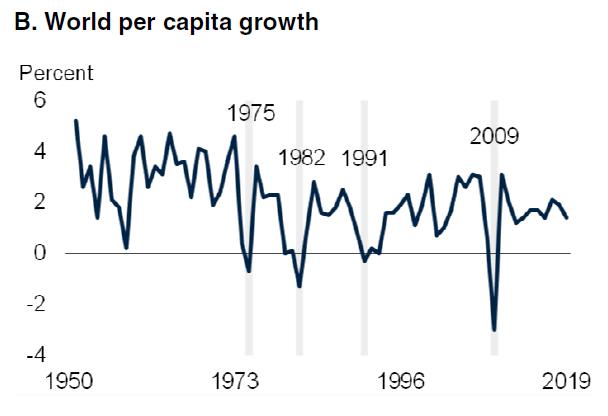
Şekil 2: G20 Ekonomilerinde Kâr Oranı 1950-2019 [33]
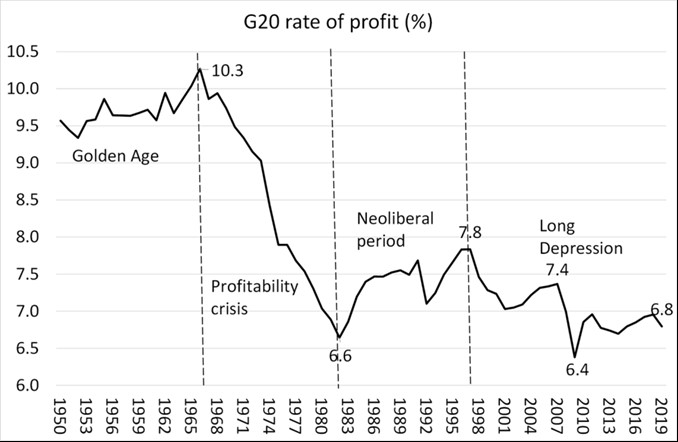
El imperialismo: ¿un sistema de “cooperación antagónica” o de contradicciones antagónicas?
Respuesta a una contribución de Promise Li a la teoría marxista del imperialismo
Un ensayo (con 8 tablas y 2 figuras) de Michael Pröbsting, 23 de noviembre de 2024
Contenido
Introducción
Un breve resumen del concepto de imperialismo de Li como “cooperación antagónica”
¿Fueron Thalheimer y Bujarin realmente los pioneros del concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica”?
Una base metodológica defectuosa: la teoría no dialéctica del equilibrio de Bujarin
Una crítica desde el punto de vista de la dialéctica materialista
El capitalismo en el siglo XXI: ¿restaurando su dinámica de crecimiento?
¿Sobreestimamos el ascenso del imperialismo chino y ruso?
¿Es la interdependencia capitalista un obstáculo para la guerra interimperialista?
Conclusiones
* * * * *
Introducción
Como señalé recientemente en una respuesta al economista argentino Claudio Katz, el debate entre los marxistas sobre la teoría del imperialismo se ha intensificado en los últimos años. (1) Hace unas semanas, otro escritor socialista, Promise Li, publicó otra contribución a este debate. (2)
Promise Li es un socialista de Hong Kong que ahora reside en Los Ángeles, donde es miembro activo de Tempest Collective y Solidarity (U.S.). Su contribución es una elaboración de su concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica” que distingue, por un lado, de aquellos que consideran al “Imperio estadounidense” como la única fuerza imperialista y, por otro lado, de aquellos que apoyan la teoría ortodoxa del imperialismo de Lenin. Como se refiere a mí (correctamente) como partidario de este último bando, me gustaría responder a su crítica. Ilustraré –tanto metodológicamente como empíricamente– que el concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica” no permite comprender la dinámica de la situación mundial en el período actual.
Como se trata de un tema amplio, trataré de limitarme a tratar los argumentos y críticas específicos presentados por Li. Para una elaboración más completa de mi comprensión de la teoría marxista del imperialismo, remito a los lectores a trabajos anteriores. (3)
Un breve resumen del concepto de imperialismo de Li como “cooperación antagónica”
En primer lugar, me gustaría señalar que Promise Li, a diferencia de otros participantes en el debate, rechaza sistemáticamente cualquier acuerdo con el imperialismo chino. Como señaló en una entrevista, “la izquierda debe centrarse en construir vínculos entre quienes resisten a los imperialismos estadounidense y chino”. (4) Por lo tanto, se distingue positivamente de los escritores (proto)estalinistas que adhieren a un antiimperialismo miope que denuncia enérgicamente los crímenes de Washington, pero es muy comedido cuando se trata de los crímenes de Pekín y Moscú. Sin duda, la experiencia de primera mano de Li con la brutal realidad del régimen de Xi en Hong Kong ha sido bastante útil para su comprensión.
Sin embargo, su concepto de imperialismo es problemático, ya que minimiza la creciente rivalidad interimperialista y sobreestima la estabilidad y la cooperación entre las grandes potencias. En cambio, considero que el sistema mundial capitalista está en decadencia a largo plazo. En un período como éste, las contradicciones entre las potencias imperialistas de Occidente y Oriente (Estados Unidos, Europa occidental, Japón, China y Rusia), así como entre estas potencias y los países semicoloniales, no pueden sino intensificarse. El imperialismo no es un sistema caracterizado por una “cooperación antagónica”, sino más bien por contradicciones antagónicas.
Antes de analizar las fallas del concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica”, comenzaremos con un resumen de la presentación de Li. Relaciona los orígenes de su teoría con los escritos del comunista alemán August Thalheimer y Nikolai Bukharin, un destacado teórico bolchevique. El concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica” fue retomado posteriormente por el colectivo marxista brasileño Política Operária (POLOP), al que pertenecía, entre otros, Ruy Mauro Marini, más conocido por su teoría del subimperialismo.
Cabe señalar de paso que la teoría del subimperialismo, al igual que el concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica”, carece de un enfoque dialéctico. Sin embargo, en este punto no abordaremos esta cuestión y remitiremos a los lectores a otros trabajos en los que tratamos la teoría del subimperialismo. (5)
Partiendo de esa base metodológica, Promise Li aplica este concepto para analizar el orden mundial imperialista actual. “Podemos modificar la definición de Thalheimer y considerar la cooperación antagónica como una etapa particular del imperialismo en la que los términos de la competencia entre capitales nacionales toman forma a través de, o están mediados por, la “interpenetración de intereses y dominios imperiales mutuos”, en lugar de considerar la cooperación y la competencia como tendencias distintas”.
En relación con esto, el autor enfatiza la relativa estabilidad del sistema mundial capitalista. Por supuesto, reconoce su crisis repetida, sin embargo, piensa que prevalece la tendencia hacia la cooperación entre las potencias.
“Sin restar importancia a la amenaza siempre presente de crisis antagónicas y rivalidades entre estados, este análisis pone de relieve la capacidad del sistema imperialista mundial de mantener dinámicas cooperativas para maximizar las vías de acumulación global”.
En consecuencia, Li delinea su concepto de otras teorías como, por un lado, la de que un “Imperio liderado por Estados Unidos” dominaría el mundo y, por otro lado, de la teoría marxista ortodoxa del imperialismo.
“No debemos pasar por alto el reajuste del capitalismo de su propia constitución para desarrollar nuevos términos para la recuperación y la estabilización. La cooperación antagónica, un marco conceptual desarrollado por los marxistas en Alemania y Brasil de posguerra, proporciona las mejores herramientas para analizar esta etapa particular del imperialismo. A diferencia de la teorización unipolar de la Tricontinental o la rivalidad multipolar de quienes siguen a los teóricos bolcheviques, que enfatizan demasiado la rivalidad entre potencias imperialistas, la cooperación antagónica entiende el sistema imperialista como una totalidad interdependiente que puede dar cabida a la interdependencia entre bloques geopolíticos y más allá de ellos. Además, a diferencia de los dos modelos descritos anteriormente, la cooperación antagónica también permite la heterogeneidad de las relaciones de poder dentro de este paradigma, aun cuando la estructura general de dependencia entre las economías centrales y periféricas sigue existiendo. Por un lado, la rivalidad entre Estados Unidos y China no implica su igualdad en el sistema imperialista global, que todavía está dirigido y dominado por los primeros. Lo que Claudio Katz llama “imperios en formación”, y otros países intermedios o subimperiales, también están cultivando la capacidad de controlar ocasionalmente el poder estadounidense a través de medios militares, económicos o de otro tipo. Pero esto no indica ni una afrenta antiimperialista a la hegemonía estadounidense ni una igualdad directa del campo de juego como un nuevo terreno de rivalidad interimperialista”.
“La interdependencia económica ha demostrado una sorprendente capacidad de recuperación incluso entre bloques geopolíticos rivales. Las teorías existentes sobre el imperialismo no logran dar cuenta plenamente de estas dimensiones aparentemente contradictorias del sistema mundial actual. Tricontinental teoriza la etapa actual del imperialismo como “hiperimperialismo”, caracterizada por un “bloque militar liderado por Estados Unidos” unipolar como la única fuerza imperialista que hace que todas las demás contradicciones globales sean secundarias o “no antagónicas”. Para los autores de Tricontinental, este bloque imperialista está siendo desafiado por una “agrupación socialista liderada por China” multipolar, que representa “las crecientes aspiraciones de soberanía nacional, modernización económica y multilateralismo, que surgen del Sur Global”. Esta perspectiva no tiene en cuenta las implicaciones tanto de la interdependencia entre los dos bloques como del papel emergente de ciertas economías intermedias –por ejemplo, Irán, los Emiratos Árabes Unidos y Rusia– en el desarrollo de hegemonías regionales que facilitan el imperialismo en medio de tensiones geopolíticas.
En contraste con la teoría tricontinental, algunos ven la forma del imperialismo actual como un conflicto interimperialista en la misma línea de la Primera Guerra Mundial, que los revolucionarios bolcheviques V. I. Lenin y Nikolai Bujarin teorizaron por primera vez. Esta visión minimiza excesivamente el declive de la hegemonía estadounidense y sobreestima el ascenso de nuevos imperialistas como contrapeso al imperialismo estadounidense. Estas concepciones erróneas son dos caras de la misma moneda: exageran la dinámica de la rivalidad, oscureciendo así los sitios salientes de interconexión en el sistema imperialista que pueden generar poderosas oportunidades de solidaridad entre luchas antisistémicas.
¿Fueron Thalheimer y Bujarin realmente los pioneros del concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica”?
¿Quiénes fueron Bujarin y Thalheimer? Bujarin se unió a los bolcheviques cuando era un militante joven y dedicado y trabajó en el partido clandestino de Moscú antes de unirse a otros revolucionarios rusos en el exilio. Se convirtió en líder bolchevique en 1917 y fue una figura clave en la formulación de la política del partido en la primera década después de la revolución. Bujarin era un teórico talentoso que chocó repetidamente con Lenin en cuestiones como la teoría del imperialismo, la teoría del Estado y la cuestión nacional. Sin embargo, era un intelectual marxista reflexivo e inspirador y Lenin apreciaba su trabajo, llamándolo incluso “el niño mimado del partido”.
Bujarin fue inicialmente portavoz del ala ultraizquierdista del partido, pero en 1923 se unió a la facción de Stalin y desempeñó un papel crucial en la teorización de la estrategia oportunista de la Comintern, la política pro-Kulak del régimen y la expulsión de la Oposición de Izquierda dirigida por León Trotsky. Sin embargo, poco después de la represión de los bolcheviques auténticos a fines de 1927, la burocracia estalinista, que enfrentaba una crisis económica como resultado de su política anterior pro-Kulak, se inclinó hacia la colectivización forzada del campesinado y la superindustrialización. En consecuencia, Stalin –a quien Bujarin ahora consideraba un “nuevo Gengis Kan”– también expulsó al antiguo “favorito del partido”. Sin embargo, a diferencia de los trotskistas, Bujarin y sus partidarios se abstuvieron de lanzar una lucha de oposición y rápidamente capitularon ante Stalin. Éste fue el fin de Bujarin como político independiente y unos años más tarde, durante los horribles juicios-espectáculo de 1936-38, todos fueron fusilados. (6)
August Thalheimer formó parte del ala izquierda de la socialdemocracia alemana antes de 1914 y se unió a la Liga Espartaco de Rosa Luxemburg y Karl Liebknecht durante la Primera Guerra Mundial. Se convirtió en el principal teórico del Partido Comunista en 1921, cuando él y Heinrich Brandler asumieron la dirección. Sin embargo, como fracasaron miserablemente en la situación revolucionaria de la segunda mitad de 1923 (el “Octubre alemán”, que no tuvo lugar), tuvieron que retirarse de las funciones de dirección. Después de la caída de su mentor intelectual Bujarin en 1928, Brandler y Thalheimer formaron la llamada Oposición de Derecha internacional, que criticó a los estalinistas sólo por sus errores ultraizquierdistas (pero no oportunistas) y no llamó a una lucha de oposición contra el régimen. Peor aún, a mediados de los años 30 apoyaron plenamente la política archioportunista del frente popular y se negaron a condenar los juicios-espectáculo de Moscú. No es de sorprender que la Oposición de Derecha internacional se desmoronara a fines de los años 30 y que sólo un pequeño grupo siguiera existiendo en Alemania después de la Segunda Guerra Mundial. (7)
A pesar de sus fallas metodológicas, Bujarin y Thalheimer –el primero mucho más que el segundo– fueron teóricos serios que hicieron una serie de contribuciones reflexivas.
El concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica” que Promise Li y el colectivo POLOP se basan en un panfleto en alemán de Thalheimer –“Grundlinien und Grundbegriffe der Weltpolitik nach dem 2. WeItkrieg” (Principios y conceptos básicos de la política mundial después de la Segunda Guerra Mundial)– que había publicado en 1946. En este panfleto, el comunista alemán llamaba a la alianza imperialista liderada por los EE.UU. “cooperación antagónica”.
Sin embargo, si bien es cierto que este término se origina en el panfleto de Thalheimer, la referencia de POLOP y Li a este documento es altamente problemática. En esta obra, el comunista alemán vio su término “cooperación antagónica” como una descripción de la situación después de la Segunda Guerra Mundial. Pero reconoció que la cooperación entre las potencias imperialistas se basaba a) en las contradicciones de clase dominantes entre las potencias occidentales y el campo estalinista en expansión y b) en la superioridad absoluta de los EE.UU. Por lo tanto, su análisis de la cooperación interimperialista se basaba en estas características coyunturales.
En consecuencia, la visión de Thalheimer del orden mundial no era la de la “cooperación”, sino más bien la de la inminente Tercera Guerra Mundial, ya que la alianza imperialista se basaba en la agresión colectiva contra el campo estalinista, es decir, los estados obreros degenerados.
“Hemos mostrado los factores que han hecho que el afán de expansión territorial de los imperialistas no resulte en una guerra dentro del campo capitalista, sino principalmente en la cooperación imperialista en diferentes grados. Por lo tanto, este afán de expansión territorial sólo puede dirigirse externamente: contra el sector socialista, la Unión Soviética y su esfera de influencia”.
“Si estos hechos muestran algo es que, inmediatamente después de la Segunda Guerra Mundial, el despliegue general en curso para una nueva guerra mundial”. (8)
Sin embargo, la interpretación que Li da al concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica” es diferente. Esa cooperación ya no puede basarse en una política común de agresión contra un enemigo común, puesto que la URSS y sus aliados ya no existen desde hace tres décadas. Por lo tanto, Li considera la “cooperación antagónica” como una nueva etapa del imperialismo, independiente de la existencia de un enemigo común que mantendría unidas a las potencias imperialistas (como el campo estalinista dirigido por la URSS en 1945-1991). En cambio, Thalheimer elaboró su concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica” como una descripción coyuntural de una situación específica causada por las características peculiares del resultado de la Segunda Guerra Mundial. Para el comunista alemán, esa situación de “cooperación antagónica” ya no existiría cuando el enemigo común hubiera desaparecido.
Del mismo modo, el peculiar análisis de Bujarin sobre el imperialismo, que ciertamente no está exento de defectos, no tenía en absoluto un enfoque que se acercara al concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica” defendido por Li. Lejos de suponer un mundo relativamente estable o incluso una cooperación predominante entre las grandes potencias, él veía más bien al imperialismo como un sistema antagónico caracterizado por una aguda rivalidad interimperialista y una tendencia a la guerra entre ellas.
“Las fricciones y conflictos que surgen fatalmente entre los grupos nacionales de la burguesía conducen, al desarrollarse a la guerra, como único medio, según los medios dirigentes, de resolver la cuestión. Como lo hemos visto, estas fricciones y conflictos son debidos a modificaciones sobrevenidas en las condiciones de reproducción del capital mundial. La sociedad capitalista, edificada sobre un conglomerado de elementos antagónicos, no puede mantenerse en un equilibrio relativo sino al precio de crisis dolorosas”. (9)
“La transición a un sistema de capitalismo financiero reforzó constantemente el proceso por el cual la simple competencia horizontal de mercado se transformó en una competencia compleja. “Como el método de lucha corresponde al tipo de competencia, esto fue inevitablemente seguido por el ‘agravamiento’ de las relaciones en el mercado mundial. Los métodos de presión directa acompañan a la competencia vertical y horizontal, por lo tanto, el sistema del capital financiero mundial implica inevitablemente una lucha armada entre rivales imperialistas. Y aquí radican las raíces fundamentales del imperialismo. (…) El conflicto entre el desarrollo de las fuerzas productivas y las relaciones capitalistas de producción debe –mientras todo el sistema no explote– reducir temporalmente las fuerzas productivas para que el siguiente ciclo de su desarrollo pueda comenzar entonces en el mismo caparazón capitalista. Esta destrucción de las fuerzas productivas constituye la condición sine qua non del desarrollo capitalista y desde este punto de vista las crisis, los costos de la competencia y –un caso particular de esos costos– las guerras son los inevitables faux frais de la reproducción capitalista”. (10)
Como podemos ver, Bujarin –a diferencia de Li– no vio la internacionalización de la producción y reproducción capitalistas como una característica que limitaría las tensiones interimperialistas. Más bien, lo entendía como un desarrollo que aceleraría los conflictos entre las grandes potencias.
“La división internacional del trabajo, la diferencia de las condiciones naturales y sociales, es un prius económico que no puede ser suprimido nu aun por una guerra mundial. Por esta razón existen allí elementos-valores bien definidos y, por consiguiente, las condiciones necesarias para la obtención de un beneficio máximo en el proceso de las operaciones internacionales. De este modo la evolución ultetrior no terminará en una "autarquía" económica, sino en el desarrollo de las relaciones internacionales, al mismo tiempo que en una mayor cohesión nacional y en la aparición de nuevos conflictos en el terreno de la concurrencia mundial”. (11)
Por lo tanto, el teórico bolchevique caracterizó la guerra como una “ley inmanente” del imperialismo: “En la sociedad capitalista, la guerra no es, en verdad, sino uno de los métodos de competencia capitalista aplicado a la esfera de la economía mundial. La guerra resulta así la ley inmanente de una sociedad que vive bajo la presión de las leyes ciegas del mercado mundial, que se desarrolla caóticamente y no de una sociedad que rige conscientemente el proceso de producción y de cambio”. (12)
En resumen, creemos que la referencia de Li y POLOP a Thalheimer y Bujarin como pioneros del concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica” carece de justificación.
Una base metodológica defectuosa: la teoría no dialéctica del equilibrio de Bujarin
Dicho esto, no negamos que también exista un elemento de justificación cuando Li señala los escritos de Bujarin y Thalheimer. Esto se debe a que el concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica” comparte ciertas similitudes metodológicas en su modo de pensar con estos dos teóricos. Es decir, todos ellos adoptan –consciente o inconscientemente– la teoría mecanicista del equilibrio que está desprovista de dialéctica.
Como se citó anteriormente, el “análisis [de Li] pone en primer plano la capacidad del sistema mundial imperialista para mantener dinámicas cooperativas para maximizar vías de acumulación global”. Asimismo, cita con aprobación a otro escritor que dice que “prevalece la cooperación [entre los imperialistas, Ed.] para el mantenimiento del sistema”:
“Como escribe Sachs: ‘La cooperación antagónica no libera al mundo capitalista de los choques internos en todos los niveles, altibajos. Hay momentos en que el antagonismo parece predominar, cuando las burguesías nacionales amenazan con una política exterior “independiente”, se rebelan contra los planes del Fondo Monetario Internacional y nacionalizan empresas extranjeras particularmente impopulares. El mismo fenómeno ocurre entre las propias potencias imperialistas en momentos de relajación periódica de la tensión internacional. Desaparece cuando hay un nuevo recrudecimiento de la tensión internacional y, como en Francia en 1968, cuando el régimen capitalista se ve en jaque. A largo plazo, prevalece la cooperación para el mantenimiento del sistema”.
Si bien, como se mencionó antes, Bujarin no estaba de acuerdo con cualquier visión del mundo imperialista como un mundo de cooperación, de hecho, simpatizaba con las enseñanzas filosóficas de Alexander Bogdanov, quien se oponía al materialismo dialéctico y elaboraba un sistema llamado “filosofía organizacional”. Bogdánov fue una figura destacada entre los bolcheviques en los años 1904-08, pero Lenin tuvo que librar una lucha feroz contra él y su filosofía cuando las diferencias políticas (combinaba su filosofía idealista con el apoyo a la política ultraizquierdista después de la derrota de la primera revolución rusa en 1905-1907) amenazaron con paralizar el partido. La famosa obra filosófica de Lenin “Materialismo y empiriocriticismo” es básicamente una polémica contra la filosofía de Bogdánov, que carecía tanto de materialismo como de dialéctica. (13)
Bujarin –sobre quien Lenin señaló en su testamento que “nunca ha estudiado la dialéctica y, creo, nunca la ha apreciado plenamente”– adoptó la teoría del equilibrio de Bogdánov. Esta teoría básicamente considera la realidad como un equilibrio (relativo, móvil) que, repetidamente, se ve perturbado por crisis repentinas y, después de algún tiempo, se restablece como un nuevo equilibrio. En otras palabras, el equilibrio sería la posición natural de las cosas. En su libro “Materialismo histórico” Bujarin expresa esta opinión de manera bastante explícita.
“Por otra parte, observamos igualmente aquí la "forma" de estos procesos: en primer lugar, el estado de equilibrio; en segundo lugar, la ruptura de este equilibrio; en tercer lugar, el restablecimiento del equilibrio sobre una "nueva" base. Luego la historia recomienza: el nuevo equilibrio es el punto de partida para una nueva alteración, así, ad infinitum.” (14)
Esto no significa que Bujarin ignorara las contradicciones y el movimiento resultante como fuerzas impulsoras cruciales del desarrollo. Sin embargo, él consideraba las contradicciones no tanto como una característica interna y esencial de todas las cosas (incluido el equilibrio), sino más bien como algo externo. Esto se debe a que ignoraba la unidad de los contrarios y la lucha entre sus partes contradictorias como la ley fundamental para comprender la materia y su movimiento. “El desarrollo es “la lucha” de los contrarios”, como dijo Lenin. (15) Por lo tanto, para Bujarin el movimiento no era causado tanto por contradicciones internas como por contradicciones entre diferentes cosas (equilibrios).
Así lo escribió en dicho libro. “Si en una "coyuntura de crecimiento" la estructura de la sociedad se empobreciera y sus desórdenes internos aumentaran, evidenciaría la existencia de una nueva contradicción entre el equilibrio externo y el interno. ¿Qué ocurriría entonces? Si la sociedad ha de continuar creciendo, se verá obligada a reconstruirse y a adaptar su estructura interna al carácter del equilibrio externo. En consecuencia, el equilibrio interno (estructural) es un factor dependiente del equilibrio externo; es una "función" de éste”. (16)
“La concepción precisa del equilibrio es más o menos la siguiente: " Decimos que un sistema se halla en estado de equilibrio cuando no puede, sin el concurso de una energía exterior, salir de tal estado". (17)
Por supuesto, Bujarin no negó explícitamente el papel de las contradicciones internas. Era un intelectual marxista demasiado inteligente para eso. Pero a pesar de sus intenciones, subestimó sistemáticamente el papel decisivo de las contradicciones internas como la principal fuerza impulsora del movimiento.
Una crítica desde el punto de vista de la dialéctica materialista
La conexión entre la teoría mecanicista del equilibrio de Bujarin y el concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica” resulta ya evidente. La filosofía de restar importancia a la lucha de contrarios y a las contradicciones internas que provocan el movimiento conduce a una comprensión de la realidad como un estado de equilibrio (en movimiento). Sobre una base metodológica de este tipo, uno acaba fácilmente por considerar la situación mundial como una situación caracterizada principalmente por una relativa estabilidad y cooperación entre los imperialistas. Como resultado, uno se confunde y no puede reconocer la dirección del movimiento de la política y la economía mundiales.
El método mecanicista es incapaz de responder correctamente a una pregunta crucial: ¿cuál es la característica determinante de la materia: un estado de equilibrio o una contradicción, un movimiento como resultado de la lucha de contrarios? Desde el punto de vista de la dialéctica materialista, la respuesta correcta es que la lucha de contrarios, la contradicción, es la característica determinante, ya que causa movimiento, transformación, progreso. En cambio, el estado de equilibrio es sólo un momento temporal. Hegel tenía toda la razón cuando decía: “la contradicción es la raíz de todo movimiento y vitalidad; solamente en la medida en que algo tiene dentro de sí mismo una contradicción se mueve, tiene impulso y actividad”. (18)
Esta era también la idea de Marx y Engels. Este último lo explicó en su “Anti-Dühring”:
“El movimiento es el modo de existencia de la materia. Jamás y en ningún lugar ha habido materia sin movimiento, ni puede haberla. Movimiento en el espacio cósmico, movimiento mecánico de masas menores en cada cuerpo celeste, vibraciones moleculares como calor, o como corriente eléctrica o magnética, descomposición y composición químicas, vida orgánica: todo átomo de materia del mundo y en cada momento dado se encuentra en una u otra de esas formas de movimiento, o en varias a la vez. Todo reposo, todo equilibrio es exclusivamente relativo, y no tiene sentido más que respecto de tal o cual forma determinada de movimiento. (...) La materia sin movimiento es tan impensable como el movimiento sin la materia. El movimiento es, por tanto, tan increable y tan indestructible como la materia misma.” (19)
Basándose en este planteamiento, Lenin subrayó en su artículo “Sobre la cuestión de la dialéctica” que el movimiento y la lucha entre los contrarios son absolutos, mientras que la estabilidad, la unidad de los contrarios es relativa.
“La unidad (coincidencia, identidad, equivalencia) de los contrarios es condicional, temporal, transitoria, relativa. La lucha de los contrarios, que se excluyen mutuamente, es absoluta, como es absoluto el desarrollo, el movimiento”. (20)
Por tanto, la dialéctica materialista se niega a considerar el equilibrio como la condición “normal” o “básica” de la materia. Es más bien una etapa temporal en un largo proceso de movimiento. Como señaló Engels en sus estudios preliminares para su “Dialéctica de la naturaleza”:
“[T]odo movimiento suelto tiende al equilibrio, y la masa del movimiento se sobrepone nuevamente al equilibrio. (...) Todo equilibrio es puramente relativo y temporal”. (21)
Ahora es posible comprender mejor la categoría de equilibrio. Los marxistas no niegan la legitimidad de dicha categoría. Pero hay que entenderlo bien. El movimiento no se produce en el vacío, sino que es causado por la lucha de los contrarios. Esta lucha sólo puede darse si existe una relación entre estos contrarios. La totalidad de estas relaciones constituye una especie de equilibrio (temporal). Pero esta relación está en constante movimiento porque “la realidad es un 'proceso de creación y destrucción'”, como señaló Abram Deborin, el filósofo líder de la gran escuela dialéctica que dominó las discusiones filosóficas en la joven Unión Soviética en los años 20 antes de que fuera aplastada por Stalin. (22)
Por lo tanto, desde el punto de vista de la dialéctica materialista, existe una clara jerarquía dialéctica. N.A. Karev, otro filósofo destacado de la escuela de Deborin y partidario de la Oposición de Izquierda de Trotsky, explicó en una crítica a la teoría del equilibrio de Bogdanov:
“Por lo tanto, Engels no dice en absoluto que este o aquel estado de equilibrio no existiría en la realidad. Pero son provisionales, constituyen sólo momentos en el movimiento de las materias, tienen sentido sólo en relación con esta o aquella forma de momentos, son el resultado de un movimiento limitado. Por tanto, los estados de equilibrio son momentos subordinados y temporales en el proceso de movimiento y desarrollo. Lo fundamental y determinante es el movimiento.” (23)
La crítica de Karev a Bogdanov nos parece también muy apropiada para el concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica” tal como lo defienden Promise Li y POLOP.
“La teoría del equilibrio de Bogdanov se basa básicamente en el punto de vista estático y no en el dinámico, ya que reconoce como determinante el momento del estado estático y no el momento del movimiento de un cuerpo dado. La categoría de equilibrio “en movimiento” no resuelve el problema, ya que considera la movilidad como una ruptura del equilibrio y no al revés – que el estado de equilibrio es un momento provisional y relativo de estabilidad dentro del proceso de movimiento. La unidad de equilibrio y movimiento se entiende aquí enfatizando la categoría de equilibrio mientras que la dialéctica enfatiza el movimiento de un cuerpo, que siempre y en todas partes es inherente a él”. (24)
Esto nos lleva al último punto de nuestro breve digresión filosófica. Subestimar la centralidad de la lucha de contrarios que resulta en el movimiento y enfatizar demasiado el concepto de equilibrio resulta en la incapacidad de evaluar la dinámica y la dirección del desarrollo. Para un mecanicista, que se fija en el estado de equilibrio, las cosas parecen estáticas, sin mucho movimiento. En realidad, se producen profundos desarrollos “debajo de la superficie”, que sólo pueden reconocerse si se aborda dialécticamente un estado dado de cosas (un “equilibrio”) como una expresión temporal de movimientos causados por la lucha de los contrarios.
Para dar una analogía sencilla de la vida cotidiana. Si uno está cocinando agua en casa, no observará grandes cambios la mayor parte del tiempo. El agua parece invariable… hasta los momentos finales, cuando empieza a hervir. ¿Significa esto que durante el 99% del tiempo no ocurre nada y que el agua se encuentra simplemente en un estado de equilibrio? Bueno, no hace falta un doctorado en física para saber que no es así, sino que en este período se está produciendo un proceso “oculto” de calentamiento.
De manera similar, los marxistas que analizan los desarrollos en la política y la economía mundiales no deben detenerse en observar sólo aquellos fenómenos que aparecen en la superficie. Para entender la dirección del desarrollo, con rupturas y explosiones por delante, es necesario mirar más allá de la superficie e identificar los procesos de acumulación de contradicciones. Como dijo una vez Deborin: “En primer lugar, un marxista debe determinar la dirección general del desarrollo”. (25)
Sin embargo, esto sólo es posible si se aplica un método materialista y dialéctico y se evitan los esquemas doctrinarios de la teoría del equilibrio mecanicista, que sólo pintan un cuadro ilusorio de estancamiento soñoliento. Hegel señaló que el método es el “el alma y la sustancia” y que “cualquier cosa es concebida y conocida en su verdad sólo cuando está totalmente sometida al método”. (26) Y, de hecho, sin el método de la dialéctica materialista, no se puede entender la dinámica del imperialismo moderno.
Al final, el método mecanicista a la Bujarin obstruye el reconocimiento de la decadencia del capitalismo y los procesos que lo acompañan de guerras, revoluciones y contrarrevoluciones.
El capitalismo en el siglo XXI: ¿restaurando su dinámica de crecimiento?
Como ya se mencionó anteriormente, Promise Li enfatiza en su ensayo que prevalecen los elementos de cooperación entre las potencias imperialistas (y también con las burguesías nacionales en el Sur Global). Asimismo, si bien reconoce que el capitalismo enfrenta crisis repetidas, cree que también ha demostrado la capacidad de superarlas y restablecer el crecimiento (aunque dice que este no es un proceso automático sino que necesita intervención política).
“Sin embargo, tampoco debemos confundir esta interdependencia con una tendencia inerte del sistema hacia el equilibrio. En realidad, el mantenimiento de esta cooperación requiere un mantenimiento continuo, especialmente porque el sistema capitalista se ve obligado a abordar la aparición repetida de crisis derivadas de sus contradicciones internas. Las crisis de rentabilidad en los años 1970 y 2000, por ejemplo, exigieron transformaciones fundamentales en la forma en que se organiza el capitalismo para restablecer el crecimiento (y la supresión de la insurgencia de la clase trabajadora). Por lo tanto, las condiciones de la cooperación deben reinventarse conscientemente para que se puedan mantener”.
En contraste, creemos que el capitalismo ha entrado en un período de crisis de largo plazo –o una “curva de declive” (para usar una categoría del concepto de Trotsky de “la curva del desarrollo capitalista” que elaboró en un artículo reflexivo en 1923)– a mediados de la década de 1970. (27) Este proceso de crisis se ha profundizado desde la Gran Recesión de 2008/09 y el nuevo período desde entonces. (28)
Naturalmente, tal decadencia no es un proceso lineal ya que a) la reproducción capitalista procede en ciclos económicos con altibajos y b) también existen tendencias contrarias. Sin embargo, a largo plazo, prevalece la tendencia al declive, y este es un proceso que puede detectarse por numerosos hechos.
Lo más importante es que existe una profunda crisis de civilización reflejada en el devastador cambio climático con consecuencias catastróficas para sectores crecientes de la humanidad. (29) Asimismo, existe una clara tendencia al estancamiento y declive de la economía mundial capitalista, que se traduce en crecientes oleadas de migración, miseria social y más guerras. Relacionado con el mismo proceso está la militarización y rivalidad cada vez más acelerada entre las potencias imperialistas. Dos grandes guerras, en Oriente Medio y Ucrania, en las que participaron grandes potencias, directa o indirectamente, y con el potencial de extenderse a otros países, son ejemplos contundentes de ello.
Como hemos abordado estos temas en varias ocasiones, nos limitaremos a presentar algunas cifras que demuestran la dinámica decreciente de la economía mundial capitalista. Como podemos ver en las cifras de la Tabla 1 y la Figura 1, ha habido una disminución continua de las tasas de crecimiento del Producto Interno Bruto (PIB), tanto en total como per cápita, desde la década de 1950. Cabe señalar que estas tablas no incluyen las cifras de la Gran Depresión de la economía mundial que comenzó a fines de 2019 y que incluyó la peor recesión desde 1929.
Tabla 1: Crecimiento anual promedio del PIB mundial 1960-2019 (30)
1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s 2011-2017 2019
4,9% 3,93% 2,95% 2,70% 2,58% 2,75% 2,5%
Esta disminución de las tasas de crecimiento de las economías capitalistas va de la mano con, o más bien ha sido causada por, una disminución correspondiente de la tasa de ganancia, que es, en última instancia, el resultado de la disminución de la proporción de trabajo vivo y el aumento de la proporción de trabajo muerto (máquinas y materias primas) en el capital total. Como Marx señaló una vez, "esta ley, y es la ley más importante de la economía política, es que la tasa de ganancia tiene una tendencia a caer con el progreso de la producción capitalista". (32)
En la Figura 2 mostramos el desarrollo de la tasa de ganancia en las 20 economías más grandes (los estados del G20) en las últimas siete décadas. Como podemos ver, ha habido, como Marx predijo, una tendencia de largo plazo de la tasa de ganancia en las últimas siete décadas.
Por lo tanto, podemos ver claramente que el capitalismo mundial no ha recuperado sus tasas de crecimiento de épocas anteriores, a pesar de numerosas intervenciones políticas de la clase dominante y a pesar de la “cooperación antagónica”. Sigue atrapado en un largo período de estancamiento y decadencia.
¿Sobreestimamos el ascenso del imperialismo chino y ruso?
Como muestra la cita anterior, Li cree que yo y otros escritores con ideas afines “restaríamos excesivamente importancia al declive de la hegemonía estadounidense mientras sobrestimamos el ascenso de nuevos imperialistas como contrapeso al imperialismo estadounidense”. Lamentablemente, no proporciona una sola cita para probar su afirmación. Por lo tanto, no tengo la menor idea de por qué Li piensa que subestimo el declive de la hegemonía estadounidense. En cualquier caso, creo que su crítica no está justificada.
Demostramos en varias obras que la clase capitalista de China no solo pudo enriquecerse masivamente a costa de la clase trabajadora nacional, sino que también pudo desafiar a los EE. UU. en el mercado mundial. Nuevamente, me limitaré a demostrar esta evolución con algunas cifras y remito a los lectores interesados a estudios más elaborados. (34)
En las tablas siguientes mostramos que China ha alcanzado rápidamente al hegemón de larga data: el imperialismo estadounidense. En la Tabla 2 vemos que la participación de China en la producción manufacturera mundial era menos de la mitad de la de Estados Unidos en el año 2000 (9,8% frente a 23,7%); sin embargo, en 2022, su participación ya era casi el doble de la de su rival occidental (30,7% frente a 16,1%).
Tabla 2. Los seis principales países en el sector manufacturero mundial, 2000 y 2022 (35)
Posición País Participación 2000 Participación 2022
1. China 9,8% 30,7%
2. EE. UU. 23,7% 16,1%
3. Japón 10,2% 6,0%
4. Aleman ia 6,4% 4,8%
5. Corea del Sur 2,5% 3,1%
6. India 1,4% 3,1%
Vemos un panorama similar cuando observamos la composición nacional de las principales corporaciones del mundo, así como la clasificación mundial de multimillonarios (Tabla 3-5). En todas estas categorías, China se ha convertido en el número 1 o 2, por delante o por detrás de EE. UU.
Tabla 3. Los 10 principales países según la clasificación de las empresas de Fortune Global 500 (2023) (36)
Posición País Empresas Participación (en %)
1 Estados Unidos 136 27,2 %
2 China (excluido Taiwán) 135 27,0 %
3 Japón 41 8,2 %
4 Alemania 30 6,0 %
5 Francia 23 4,6 %
6 Corea del Sur 18 3,6 %
7 Reino Unido 15 3,0 %
8 Canadá 14 2,8 %
9 Suiza 11 2,2 %
10 Países Bajos 10 2,0 %
Tabla 4. Los 5 principales países de la lista Forbes Billionaires 2023 (37)
Posición País Número de multimillonarios
1 Estados Unidos 735
2 China (incl. Hong Kong) 561
3 India 169
4 Alemania 126
5 Rusia 105
Tabla 5. Los 10 países más ricos de la lista Hurun Global Rich List 2024 (38)
Posición País Número de multimillonarios
1 China (incl. Hong Kong) 814
2 EE. UU. 800
3 India 271
4 Reino Unido 146
5 Alemania 140
6. Suiza 106
7. Rusia 76
8. Italia 69
9. Francia 68
10. Brasil 64
Rusia ha desarrollado también un capital monopolista que domina el mercado interno y que exporta capital a varios países, principalmente de Asia Central y Europa del Este. Su fortaleza económica también ha quedado demostrada por el hecho de que ha logrado resistir una ola de sanciones sin precedentes por parte de todas las potencias occidentales (debido a la guerra en Ucrania) durante casi tres años. Sin embargo, su posición en el mercado mundial es sustancialmente más débil, aunque recientemente ha superado el PIB de Alemania y Japón en términos de PPP (paridad de poder adquisitivo). (39)
Si bien Rusia está claramente por detrás de Estados Unidos y China en términos económicos, es una potencia líder en el campo militar. Tiene el mayor arsenal nuclear y el tercer gasto militar más alto. (Véase los cuadros 6 y 7) Además, ha demostrado su agresividad militar en numerosas intervenciones militares en otros países con el fin de ampliar su influencia, sofocar rebeliones populares o mantener en el poder una dictadura aliada (por ejemplo, Chechenia, Georgia, Kazajstán, Siria, Libia, Malí, etc.) (40)
Tabla 6. Fuerzas nucleares mundiales, 2024 (41)
País Arsenal militar total Inventario total (incl. ojivas retiradas)
Rusia 4.380 5.580
Estados Unidos 3.708 5.044
China 500 500
Francia 280 290
Reino Unido 225 225
India 172 172
Pakistán 170 170
Israel 90 90
Corea del Norte 50 50
Tabla 7. Gasto militar, en miles de millones de dólares estadounidenses como porcentaje del gasto mundial, 2023 (42)
Gasto (miles de millones de dólares) Participación en el gasto mundial
1. Estados Unidos 916 37%
2. China 296 12%
3. Rusia 109 4,5%
Además, China y Rusia han ampliado considerablemente recientemente sus esferas de influencia, como lo demuestra la ampliación de los BRICS. Cuatro estados (Egipto, Etiopía, Irán y Emiratos Árabes Unidos) se unieron formalmente a los cinco miembros originales de los BRICS (Brasil, Rusia, India, China y Sudáfrica) a principios de 2024. Se ha invitado a un país, Arabia Saudita, a unirse, pero aún no ha decidido al respecto. Y en octubre de 2024, otros 13 estados se convirtieron en los llamados "países socios" (Argelia, Bielorrusia, Bolivia, Cuba, Indonesia, Kazajstán, Malasia, Nigeria, Tailandia, Turquía, Uganda, Uzbekistán y Vietnam).
Como expliqué con más detalle en mi respuesta a Claudi Katz antes mencionada, los BRICS+ tenían, después de su expansión a nueve estados miembros en 2023, una población combinada de alrededor de 3.500 millones, o el 45% de la población mundial (y ahora es más de la mitad si se incluyen los nuevos "países socios"). Su PIB combinado, dependiendo del método de cálculo, es un poco más de 1/3 detrás de las Grandes Potencias occidentales (G7) o ya ha superado a las antiguas potencias imperialistas. Asimismo, los BRICS+ representan el 38,3% de la producción industrial mundial total, el principal sector de la producción de valor capitalista.
En cuanto a las fuentes de energía, los miembros del BRICS+ poseen el 47% de las reservas mundiales de petróleo y el 50% de sus reservas de gas natural. (43) A partir de 2024, los BRICS, junto con sus nuevos miembros, controlan aproximadamente el 72% de las reservas mundiales de metales de tierras raras. (44)
Por supuesto, es cierto que los BRICS+ no son una alianza homogénea y centralizada. Aun así, se trata de un “grupo no occidental”, como destacaron Modi y Putin, que está dominado por el imperialismo chino y ruso. Además, los países BRICS+ están menos desarrollados desde el punto de vista capitalista y tienen un nivel de vida más bajo.
Sin embargo, aunque Li piensa que sobreestimo el ascenso de China y Rusia como nuevas potencias imperialistas, creo que subestima este proceso y, en consecuencia, también subestima la aceleración de la rivalidad interimperialista. Las amenazas militares y el ruido de sables nucleares entre la OTAN y Rusia, así como las crecientes tensiones militares entre Washington y Pekín en el Mar de China Meridional y en torno a Taiwán, son indicaciones claras de que el sistema imperialista no se caracteriza tanto por una “cooperación antagónica” como por contradicciones antagónicas.
Por lo tanto, no es sorprendente que, como informa el SIPRI, el gasto militar global aumente año tras año desde mediados de la década de 1990 y ahora, con un total de 2.443 billones de dólares, sea aproximadamente el doble de lo que era hace 30 años. (45)
La creciente rivalidad interimperialista no se limita al armamento y las tensiones militares. También hay una creciente guerra comercial entre Estados Unidos, China, la UE y Rusia combinada con un creciente proteccionismo. De hecho, la globalización ha terminado desde la Gran Recesión de 2008, después de décadas de crecimiento masivo (“Globalización”). Desde entonces, es decir, durante más de 15 años, el comercio mundial de mercancías ha disminuido como porcentaje de la producción mundial del 51,2% (2008) al 45,8% (2023). (46)
Por lo tanto, cuando Li dice que “lejos de deshacer el orden mundial neoliberal, la clase capitalista innova nuevos términos para mantener y reformar la globalización”, no entiende completamente la dirección del desarrollo de las relaciones entre las potencias imperialistas.
Por todas estas razones, es difícil entender por qué Li se opone a la categoría de una “nueva guerra fría” entre las potencias occidentales y orientales, calificándola de “ficción ideológica”. ¿No ve el creciente militarismo y la aceleración de la rivalidad que apuntan a otra guerra mundial entre las potencias imperialistas?
Como insistí antes, los marxistas deben “determinar la dirección general del desarrollo” para comprender las rupturas y explosiones venideras. El concepto de Li del imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica” no ayuda a comprender la dinámica de la situación mundial actual.
¿Es la interdependencia capitalista un obstáculo para la guerra interimperialista?
Tratemos finalmente otro argumento importante que plantea Li en su ensayo. Como se muestra en las citas anteriores, sostiene que la “interdependencia económica” ha sido una característica clave del imperialismo moderno y, como resultado, esto constituiría la base material para la “cooperación antagónica” entre las potencias. Incluso piensa que tal interdependencia económica haría imposible o al menos improbable una guerra interimperialista.
“De hecho, la integración económica global todavía existía en formas salientes durante la Primera Guerra Mundial, pero en su mayoría contenida dentro de campos geopolíticos, lo que el historiador Jamie Martin llama “interdependencia tensa”. Sin embargo, el ascenso del neoliberalismo ha desarrollado un nivel de interdependencia que perdura incluso entre bloques de estados rivales, socavando así la posibilidad de una guerra interimperialista abierta presenciada en las primeras dos guerras mundiales”.
Creemos que esto es incorrecto, tanto metodológicamente como históricamente. Como señaló Bujarin correctamente en las citas mencionadas anteriormente, la interdependencia no sólo profundiza los vínculos económicos, sino que también acelera la rivalidad. En los últimos años, China y los Estados Unidos han sido socios comerciales entre sí muy importantes. Sin embargo, esto no ha impedido que estas potencias inicien y aceleren una guerra comercial. Lo mismo ocurre ahora entre China y la Unión Europea, donde esta última ha impuesto aranceles sustanciales a las importaciones chinas. Es cierto que las grandes empresas de ambos lados no están contentas con esta evolución, pero al final tienen que subordinarse a las leyes objetivas del capitalismo y a su inherente rivalidad interimperialista.
Como expliqué en mi libro antes mencionado sobre la rivalidad entre las grandes potencias, también existe un precedente histórico de tal evolución. Gran Bretaña y Alemania, dos grandes rivales en la Primera Guerra Mundial, tenían estrechas relaciones económicas antes de 1914. (47) En la Tabla 8 vemos que Gran Bretaña era el socio comercial más importante de Alemania antes de 1914 (y Estados Unidos era el número 2), mientras que Alemania era casi tan importante como Francia para el comercio británico. Sin embargo, esa interdependencia económica no impidió que estas potencias lanzaran la guerra más devastadora entre sí.
Tabla 8. Principales socios comerciales de Gran Bretaña y Alemania, 1890-1913 (porcentaje medio de participación) (48)
Gran Bretaña Alemania
1. EE. UU.: 19,47 % 1. Gran Bretaña: 13,85 %
2. Francia: 8,99 % 2. EE. UU.: 11,03 %
3. Alemania: 8,90 % 3. Austria-Hungría: 10,15 %
Por lo tanto, a largo plazo, la creciente interdependencia económica entre las potencias imperialistas no conduce a un sistema capitalista mundial más estable. No crea un tipo de imperialismo caracterizado por la “cooperación antagónica”; el imperialismo sigue siendo, más bien, un sistema lleno de contradicciones antagónicas.
Conclusiones
1. El concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica” no permite comprender la dinámica de la situación mundial en el período actual. Si bien Promise Li reconoce correctamente la naturaleza imperialista no sólo de las antiguas potencias occidentales sino también de las nuevas potencias orientales (China y Rusia), critica erróneamente a los partidarios de la teoría ortodoxa del imperialismo por sobreestimar la rivalidad entre ellas.
2. La referencia de Promise Li y del colectivo brasileño Política Operária a August Thalheimer y Nikolai Bujarin como pioneros del concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica” es engañosa. Bujarin, a pesar de sus debilidades de esquematismo, enfatizó la rivalidad y el antagonismo entre las potencias imperialistas que inevitablemente tenían que desembocar en guerras. Es cierto que Thalheimer elaboró la tesis de la “cooperación antagónica” entre las potencias imperialistas en 1946, pero se trataba de una descripción (correcta) de una situación global específica caracterizada por a) la expansión masiva de los estados estalinistas y b) el resultado de la Segunda Guerra Mundial con los EE.UU. como hegemón absoluto entre los estados imperialistas. Por lo tanto, su tesis de una mayor cooperación entre las potencias imperialistas estaba directamente relacionada con su enfoque agresivo colectivo contra los estados estalinistas, que apuntaba a una nueva guerra mundial. Por lo tanto, Thalheimer consideraba que las tensiones interimperialistas se reducirían porque serían superadas por la aceleración masiva de las tensiones entre los estados imperialistas y los estados obreros degenerados. Sin embargo, desde que el estalinismo colapsó en 1989-91, el concepto de Thalheimer ya no es aplicable al imperialismo actual.
3. Es cierto que Bujarin, el mentor político de Thalheimer, estaba influenciado por la filosofía de Alexander Bogdanov, un acérrimo oponente del materialismo dialéctico. Por eso, defendía una visión del mundo que incorporaba la teoría mecanicista del equilibrio, un concepto que minimiza el papel de las contradicciones internas como fuerza impulsora del movimiento. En consecuencia, los partidarios de este método consideran el equilibrio como la característica principal de la materia, cuando, de hecho, es más bien movimiento. Por eso, el método bujarinista subestima las tendencias de ruptura, crisis y explosiones en la situación mundial y sobreestima su estabilidad y equilibrio. El concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica” adolece de tales deficiencias metodológicas.
4. Desde el punto de vista de la dialéctica materialista, las contradicciones internas, causadas por la unidad y la lucha de los contrarios, son la fuerza impulsora del movimiento. El método mecanicista es incapaz de responder correctamente a la pregunta: ¿cuál es la característica determinante de la materia: un estado de equilibrio o contradicción, movimiento como resultado de la lucha de los contrarios? Desde el punto de vista de la dialéctica materialista, la respuesta correcta es que la lucha de los contrarios, la contradicción es la característica determinante, ya que causa movimiento, transformación, progreso. En cambio, el estado de equilibrio es sólo un momento temporal.
5. Existe una clara conexión entre la teoría mecanicista del equilibrio de Bujarin y el concepto de imperialismo como “cooperación antagónica”. La filosofía de restar importancia a la lucha de contrarios y a las contradicciones internas que provocan el movimiento conduce a una comprensión de la realidad como un estado de equilibrio (en movimiento). Sobre una base metodológica de este tipo, uno acaba fácilmente por considerar la situación mundial como una situación caracterizada principalmente por una relativa estabilidad y cooperación entre los imperialistas. Como resultado, uno se confunde y no puede reconocer la dirección del movimiento de la política y la economía mundiales.
6. En consecuencia, Promise Li no toma suficientemente en cuenta el carácter de crisis y la decadencia del sistema imperialista mundial, tanto económica como políticamente. La economía capitalista mundial está atrapada en un estancamiento y declive a largo plazo, el cambio climático amenaza la supervivencia de la humanidad y la miseria social y las guerras se están extendiendo.
7. La crítica de Promise Li de que sobrestimamos el ascenso del imperialismo chino y ruso ignora los cambios cualitativos en la relación de fuerzas entre las grandes potencias en las últimas dos décadas. Los imperialistas orientales están desafiando seriamente la hegemonía occidental de larga data, económica, política y militarmente. De hecho, la crítica de Li está relacionada con su subestimación de la rivalidad interimperialista y su opinión de que la “cooperación antagónica” sería la característica principal de la situación mundial.
8. Promise Li afirma que la “interdependencia económica” es una característica clave del capitalismo moderno y que esto “socavaría la posibilidad de una guerra interimperialista abierta”. Sin embargo, la historia ha demostrado que esto no es cierto. A largo plazo, la creciente interdependencia económica entre las potencias imperialistas no da como resultado un sistema capitalista mundial más estable. No crea un tipo de imperialismo caracterizado por la “cooperación antagónica”; el imperialismo sigue siendo, más bien, un sistema lleno de contradicciones antagónicas.
1) Michael Pröbsting: ¿Vivimos en la era del “Imperio” o del Imperialismo? Otra respuesta a Claudio Katz sobre la actualidad de la teoría marxista del imperialismo, 16 de noviembre de 2024, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/are-we-living-in-the-age-of-empire-or-of-imperialism-3rd-reply-to-claudio-katz/#anker_1
2) Promise Li: Imperialism as Antagonistic Cooperation, 15 de octubre de 2024, https://spectrejournal.com/imperialism-as-antagonistic-cooperation/; https://links.org.au/imperialism-antagonistic-cooperation. Todas las citas son de este ensayo a menos que se indique lo contrario.
3) Mis trabajos más detallados sobre la teoría marxista del imperialismo son dos libros: Anti-imperialismo en la era de la rivalidad de las grandes potencias. Los factores detrás de la Rivalidad acelerada entre los E.U, China, Rusia, la U.E y Japón. Una crítica del análisis de la izquierda y una semblanza de la Perspectiva Marxista, RCIT Books, Vienna 2019, https://www.thecommunists.net/home/espa%C3%B1ol/libro-anti-imperialismo-en-la-era-de-la-rivalidad-de-las-grandes-potencias/; The Great Robbery of the South. Continuity and Changes in the Super-Exploitation of the Semi-Colonial World by Monopoly Capital Consequences for the Marxist Theory of Imperialism, RCIT Books, 2013, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/great-robbery-of-the-south/
4) Promise Li: US-China rivalry, ‘antagonistic cooperation’ and anti-imperialism in the 21st century, 14 September, 2023, https://links.org.au/us-china-rivalry-antagonistic-cooperation-and-anti-imperialism-21st-century
5) Para una crítica de la teoría del “subimperialismo”, véase, por ejemplo, mi ensayo: Semi-Colonial Intermediate Powers and the Theory of Sub-Imperialism. A contribution to an ongoing debate amongst Marxists and a proposal to tackle a theoretical problem, 1 August 2019, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/semi-colonial-intermediate-powers-and-the-theory-of-sub-imperialism/; ver también el Capítulo IV ("Los criterios marxistas para una gran potencia imperialista" de nuestro libro ya mencionado "Anti-imperialismo en la era de la rivalidad de las grandes potencias")
6) Biografías útiles de Bujarin son, por ejemplo, las de Stephen Cohen: Bujarin y la Revolución Bolchevique. Una Biografía Política, 1888-1938. Editores Siglo XXI; Wladislaw Hedeler: Nikolai Bucharin. Stalins tragischer Opponent. Eine politische Biographie. Matthes & Seitz, Berlin 2015; Adolf G. Löwy: El Comunismo de Bujarin. La Historia Universal es el Juicio Final, Ed. Grijalbo, 1972; Ana Lárina: Lo que no puedo olvidar, Ed. Galaxia Gutenberg, 2007.
7) Sobre la historia de la Oposición de Derecha en lengua inglesa, véase, por ejemplo: Robert J. Alexander: The Right Opposition. The Lovestoneites and the International Communist Opposition of the 1930s, Greenwood Press, London 1981
8) August Thalheimer: Grundlinien und Grundbegriffe der Weltpolitik nach dem 2. Weltkrieg, Gruppe Arbeiterpolitik, 1946, p. 11 and 9 (traducción hecha por nosotros)
9) Nicolai Bujarin: El imperialismo y la economía mundial (195), ed. Cuadernos de Pasado y Presente, Buenos Aires 1971, p. 131
10) Nikolai Bukharin: The Politics and Economics of the Transition Period (1920), Routledge, Abingdon 2003, pp. 63-64
11) Nicolai Bujarin: El imperialismo y la economía mundial (195), ed. Cuadernos de Pasado y Presente, Buenos Aires 1971, p. 185
12) Ibid, 182
13) Sobre Alexander Bogdanov ver por ejemplo James D. White: Red Hamlet: The Life and Ideas of Alexander Bogdanov, Brill, Leiden 2018; Dietrich Grille: Lenins Rivale: Bogdanov und seine Philosophie, Verlag Wissenschaft und Politik, Cologne 1966; see also the foreword of Bogdanov's Tektology Vol. 1 by Vadim N. Sadovsky and Vladimir V. Kelle, Centre for Systems Studies, University of Hull, 1996, pp. iii-xxii; V.A. Bazarov: Bogdanov as a Thinker, en: Alexander Bogdanov: Empiriomonism. Essays in Philosophy, Books 1–3, Brill, Leiden 2020, pp. xvii-xli.
14) Nikolai Bujarin: Teoría del Materialismo Histórico: Ensayo popular de sociología (1921), ed. Siglo XXI, Madrid 1974, p. 167
15) V. I. Lenin: En torno a la cuestión de la dialéctica (1915), https://www.marxists.org/espanol/lenin/obras/1910s/1915dial.htm
16) Nicolai Bujarin: Materialismo Histórico, p. 171
17) Ibid, p. 166
18) George Friedrich Wilhelm Hegel: La Ciencia de la Lógica vol. 1, ed. Abada, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid 2021, p. 491 (también citado en V. I. Lenin: Resumen del libro de Hegel "La ciencia de la lógica", en Lenin Obras Completas ed. Progreso, p. 121
19) Federico Engels: Anti-Dühring. La revolución de la ciencia por el señor Eugen Dühring, ed. Fundación Federico Engels, Madrid 2014, p 112 y 113
20) V. I. Lenin: En torno a la cuestión de la dialéctica (1915), https://www.marxists.org/espanol/lenin/obras/1910s/1915dial.htm
21) Federico Engels: Dialéctica de la naturaleza, ed. Grijalbo, México 1961, p. 210
22) Abram Deborin: Lenin als revolutionärer Dialektiker (1925); in: Nikolai Bucharin, Abram Deborin: Kontroversen über dialektischen und mechanistischen Materialismus, Frankfurt a.M. 1974, p. 54 (traducción hecha por nosotros)
23) N.A. Karew: Die Theorie des Gleichgewichts und der Marxismus; in: Wilhelm Goerdt (Hrsg.): Die Sowjetphilosophie. Wendigkeit und Bestimmtheit. Dokumente, Darmstadt 1967, p. 139 (traducción hecha por nosotros)
24) Ibid., pp. 140-141
25) Abram Deborin: Lenin als revolutionärer Dialektiker (1925); in: Unter dem Banner des Marxismus, 1. Jahrgang (1925-26), p. 224 (traducción hecha por nosotros)
26) George Friedrich Wilhelm Hegel: La Ciencia de la Lógica vol. 2, ed. Digital Titivillus, p. 508
27) León Trotsky: La Curva del Desarrollo Capitalista (1923), https://www.marxists.org/espanol/trotsky/1923/junio/21.htm
28) Para nuestro análisis del período histórico actual, véase, por ejemplo, el capítulo 14 del libro mencionado anteriormente “The Great Robbery of the South” así como los capítulos I y II del libro mencionado anteriormente “Anti-imperialismo en la era de la rivalidad de las grandes potencias”.
29) Ver, por ej., CCRI: Tesis sobre Agricultura y Ecología, septiembre de 2023, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/theses-on-agriculture-and-ecology/#anker_1, Almedina Gunić: The Deadly Breath of Imperialism, 23.10.2017, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/pollution-caused-the-death-of-9-million-people-in-2015/
30) Murray E.G. Smith, Josh Watterton: Valorization, Financialization & Crisis: A Temporal Value-Theoretic Approach, 2021, p. 5
31) M. Ayhan Kose, Franziska Ohnsorge (Eds.): A Decade since the Global Recession, Lessons and Challenges for Emerging and Developing Economies, World Bank, 2019, p. 9
32) Karl Marx: Economic Manuscripts of 1861-63. Capital and Profit. 7) General Law of the Fall in the Rate of Profit with the Progress of Capitalist Production; in: MECW, Volume 33, pp. 104-145; http://www.marxists.org/archive/marx/works/1861/economic/ch57.htm
33) Michael Roberts: Has globalisation ended? (2022), https://thenextrecession.wordpress.com/2022/04/27/has-globalisation-ended/
34) He publicado varios trabajos sobre el capitalismo en China y su ascenso a potencia imperialista. Los más importantes son los siguientes: Chinese Imperialism and the World Economy, Un ensayo publicado en la segunda edición de “The Palgrave Encyclopedia of Imperialism and Anti-Imperialism” editado por Immanuel Ness y Zak Cope), Palgrave Macmillan, Cham, 2020, https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007%2F978-3-319-91206-6_179-1; China: sobre la relación entre el Partido “comunista” y los capitalistas. Notas sobre el carácter de clase específico de la burocracia gobernante de China y su transformación en las últimas décadas, 8 de septiembre de 2024, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/china-on-the-relationship-between-communist-party-and-capitalists/#anker_1; China: sobre el estalinismo, la Restauración capitalista y la teoría marxista del Estado. Notas sobre la transformación de las relaciones sociales de propiedad bajo el régimen de un solo partido, 15 de septiembre de 2024, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/china-on-stalinism-capitalist-restoration-and-marxist-state-theory/#anker_1; China: una potencia imperialista… ¿o todavía no? ¡Una cuestión teórica con consecuencias muy prácticas! Continuando el Debate con Esteban Mercatante y el PTS/FT sobre el carácter de clase de China y sus consecuencias para la estrategia revolucionaria, 22 de eenero de 2022, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/china-imperialist-power-or-not-yet/#anker_1; China‘s transformation into an imperialist power. A study of the economic, political and military aspects of China as a Great Power (2012), in: Revolutionary Communism No. 4, https://www.thecommunists.net/publications/revcom-1-10/#anker_4; ¿Cómo es posible que algunos marxistas sigan dudando de que China se ha vuelto capitalista? (Una crítica del PTS/FT), 18 de septiembre de 2020, https://www.thecommunists.net/home/espa%C3%B1ol/pts-ft-y-imperialismo-chino-2/; Incapaces de ver el bosque por ver los árboles. El empirismo ecléctico y la falla del PTS/FT en reconocer el carácter imperialista de China, 13 de agosto de 2020, https://www.thecommunists.net/home/espa%C3%B1ol/pts-ft-y-imperialismo-chino/; China’s Emergence as an Imperialist Power (Article in the US journal 'New Politics'), in: “New Politics”, Summer 2014 (Vol:XV-1, Whole #: 57). Vea muchos más documentos del RCIT en una subpágina especial en el sitio web de la CCRI: https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/china-russia-as-imperialist-powers/
35) Cifras del año 2000: APEC: Regional Trends Analysis, May 2021, p. 2; las cifras de Alemania y la India en la primera columna son del año 2005 (UNIDO: Industrial Development Report 2011, p. 194); cifras del año 2022: UNIDO: International Yearbook of Industrial Statistics Edition 2023, pp. 36-37
36) Fortune Global 500, August 2023, https://fortune.com/ranking/global500/2023/ (las cifras en porcentaje son cálculos nuestros)
37) Forbes: Forbes Billionaires 2023, https://www.forbes.com/sites/chasewithorn/2023/04/04/forbes-37th-annual-worlds-billionaires-list-facts-and-figures-2023/?sh=23927e7477d7
38) Hurun Global Rich List 2024, 26.03.2024, https://www.hurun.net/en-US/Info/Detail?num=K851WM942LBU
39) Ver por ej. Michael Pröbsting: Russia Overtakes Japan to Become Fourth Largest Economy in the World, 5 de julio de 2024, https://www.thecommunists.net/worldwide/global/russia-overtakes-japan-to-become-fourth-largest-economy-in-the-world/
40) He publicado varias obras sobre el capitalismo en Rusia y su ascenso a potencia imperialista. Las más importantes son los siguientes folletos: Las características peculiares del imperialismo ruso. Un estudio de los monopolios, la exportación de capital y la superexplotación de Rusia a la luz de la teoría marxista, 10 de agosto de 2021, https://www.thecommunists.net/theory/the-peculiar-features-of-russian-imperialism/#anker_7; Lenin’s Theory of Imperialism and the Rise of Russia as a Great Power. On the Understanding and Misunderstanding of Today’s Inter-Imperialist Rivalry in the Light of Lenin’s Theory of Imperialism. Another Reply to Our Critics Who Deny Russia’s Imperialist Character, August 2014, http://www.thecommunists.net/theory/imperialism-theory-and-russia/; Russia as a Great Imperialist Power. The formation of Russian Monopoly Capital and its Empire, 18 March 2014, http://www.thecommunists.net/theory/imperialist-russia/.
41) SIPRI Yearbook 2024: Armaments, Disarmament and International Security, p. 272
42) Nan Tian, Diego Lopes Da Silva, Xiao Liang and Lorenzo Scarazzato: Trends in World Military Expenditure, SIPRI, 2023, p. 2
43) Ver sobre esto: Henry Meyer, S'thembile Cele, and Simone Iglesias: Putin Hosts BRICS Leaders, Showing He Is Far From Isolated, Bloomberg, 22 de octubre de 2024, https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2024-10-22/putin-hosts-brics-leaders-in-russia-defying-attempts-from-west-to-isolate-him; Dr Kalim Siddiqui: The BRICS Expansion and the End of Western Economic and Geopolitical Dominance, 30 de octubre de 2024, https://worldfinancialreview.com/the-brics-expansion-and-the-end-of-western-economic-and-geopolitical-dominance/; Walid Abuhelal: Can the Brics end US hegemony in the Middle East? Middle East Eye, 22 de octubre de 2024 https://www.middleeasteye.net/opinion/can-brics-end-us-hegemony-middle-east; Anthoni van Nieuwkerk: BRICS+ wants new world order sans shared values or identity, 30 de octubre de 2024 https://asiatimes.com/2024/10/brics-wants-new-world-order-sans-shared-values-or-identity/
44) Ben Aris: Can the BRICS beat the G7? Intellinews, 19 de octubre de 2024, https://www.intellinews.com/can-the-brics-beat-the-g7-348632/?source=south-africa
45) Nan Tian et al: Trends in World Military Expenditure, p. 2
46) World Bank: Merchandise trade (% of GDP), accessed on 21 de novieembre de 2024, https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/TG.VAL.TOTL.GD.ZS?view=chart
47) Ver por ejemplo. Helga Nussbaum: Der europäische Wirtschaftsraum. Verflechtung, Angleichung, Diskrepanz, in: Fritz Klein, Karl Otmar von Aretin (Eds): Europea um 1900, Akademie-Verlag, Berlin 1989, p. 49
48) Stefano Battilossi: The Determinants of Multinational Banking during the First Globalization, 1870-1914, Working Papers 114, Oesterreichische Nationalbank (Banco Central Austriaco), 2006, p. 40
Figura 1: Crecimiento anual promedio del PIB mundial per cápita 1950-2019 (31)

Figura 2: Tasa de ganancia en las economías del G20 1950-2019 (33)

- Loading X messages...
